FIGURE 7.
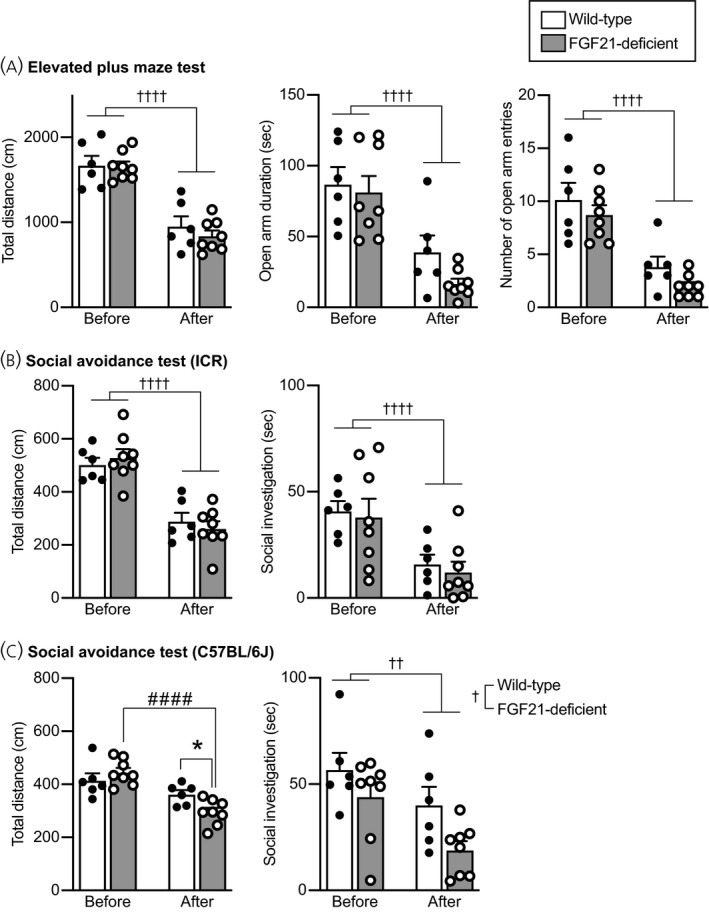
Anxiety‐related behaviours in an elevated plus maze test and social avoidance behaviours in wild‐type and FGF21‐deficient mice. A, Total distance of locomotion (Total distance), time spent for staying in the open arms (Open arm duration), and number of entries into the open arms (Number of open arm entries) in an elevated plus maze test. The values of these parameters were decreased after social defeat stress compared to the values before social defeat stress. No significant difference was found between wild‐type mice and FGF21‐deficient mice. B, Total distance of locomotion and time spent for social contact with ICR mice in a social avoidance test. Total locomotor distance and time spent for investigating a cylinder containing an ICR mouse were reduced after social defeat stress, and no significant difference was found between wild‐type mice and FGF21‐deficent mice. C, Total distance of locomotion and time spent for social contact with a C57BL/6J mouse in a social avoidance test. Total locomotion activity was reduced after social defeat stress in FGF21‐deficient mice but not in wild‐type mice, and locomotor activity after stress was significantly lower in FGF21‐deficient mice compared to wild‐type mice. The time spent for investigating a cylinder containing a C57BL/6J mouse was significantly reduced after social defeat stress, and it was significantly shorter in FGF21‐deficient mice compared to wild‐type mice. The number of wild‐type mice and FGF21‐deficient mice was 6 and 8, respectively. ††P < 0.01, ††††P < 0.0001, before stress vs after stress; †P < 0.05, wild‐type mice vs FGF21‐deficient mice, two‐way repeated measures ANOVA. #### P < 0.0001, FGF21‐deficient mice before stress vs FGF21‐deficient mice after stress; *P < 0.05, wild‐type mice after stress vs FGF21‐deficient mice after stress, two‐way repeated measures ANOVA followed by post‐hoc Bonferroni's test
