FIGURE 12.
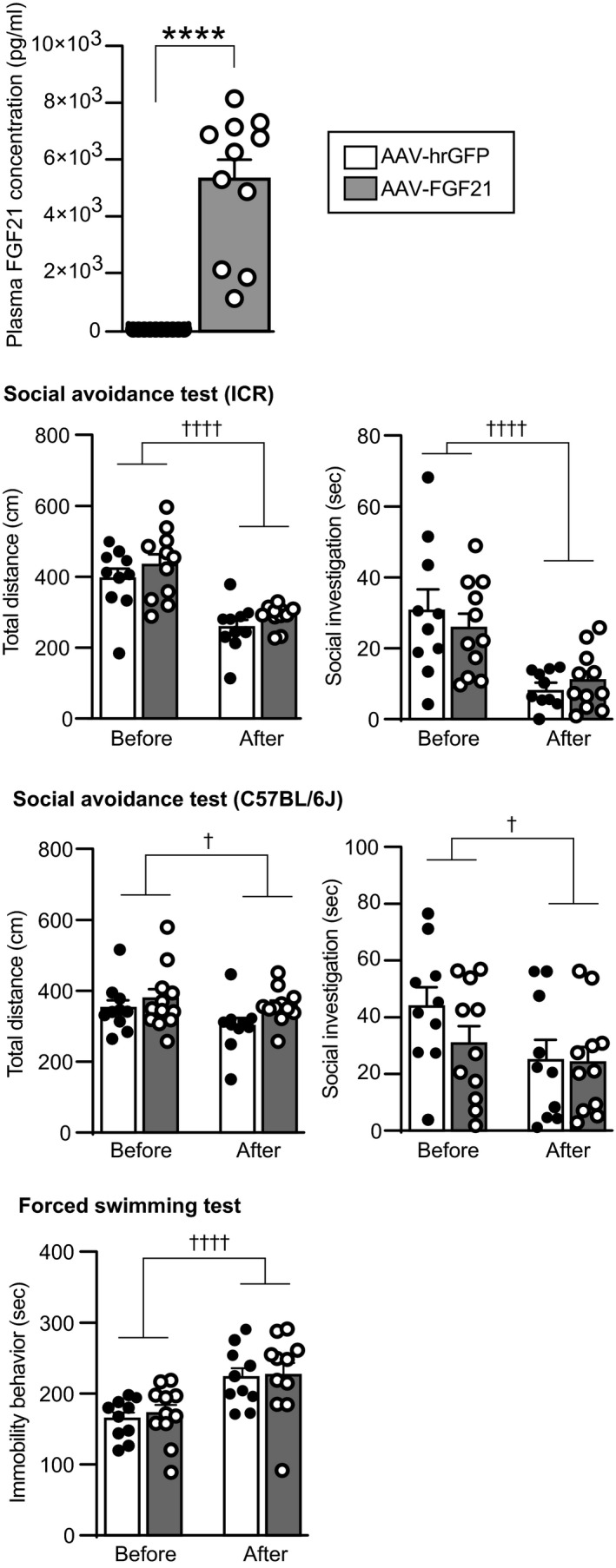
Plasma FGF21 concentrations, social avoidance behaviours and immobility behaviours in a forced swimming test in FGF21‐deficient mice injected with AAV‐hrGFP or AAV‐FGF21. Plasma concentrations of FGF21 in mice injected with AAV‐hrGFP and in mice injected with 1 × 109 vg AAV‐FGF21 are shown (top). AAV‐hrGFP or AAV‐FGF21 was injected 26 days before blood sampling. Plasma FGF21 concentrations were significantly higher after injection of AAV‐FGF21 compared to after injection of AAV‐hrGFP. Total distance of locomotion and time spent for social investigation towards ICR mice in a social avoidance test are shown (second row). Total locomotor distance and time spent for investigating a cylinder containing an ICR mouse were reduced after social defeat stress, and no significant difference was found between FGF21‐deficient mice injected with AAV‐hrGFP and FGF21‐deficient mice injected with AAV‐FGF21. Total distance of locomotion and time spent for social contact with a C57BL/6J mouse in a social avoidance test are shown (third row). Total locomotor distance and time spent for investigating a cylinder containing a C57BL/6J mouse were reduced after social defeat stress, and no significant difference was found between FGF21‐deficient mice injected with AAV‐hrGFP and FGF21‐deficient mice injected with AAV‐FGF21. Duration of immobility behaviour of FGF21‐deficient mice injected with AAV‐hrGFP or AAV‐FGF21 in a forced swimming test and differences between immobility behaviour time before social defeat stress and that after social defeat stress are shown (lowest row). Time spent for immobility behaviour in a forced swimming test was reduced after social defeat stress, although no significant difference was found between mice injected with AAV‐hrGFP and mice injected with AAV‐FGF21. The number of AAV‐hrGFP‐injected and AAV‐FGF21‐injected mice was 10 and 11. ****P < 0.0001, vs AAV‐hrGFP, Mann Whitney test. †P < 0.05, ††††P < 0.0001, vs AAV‐hrGFP, two‐way repeated measures ANOVA
