Figure 1. Genetic absence of microglia in AD mice induces premature lethality and alters cell-specific transcriptional states.
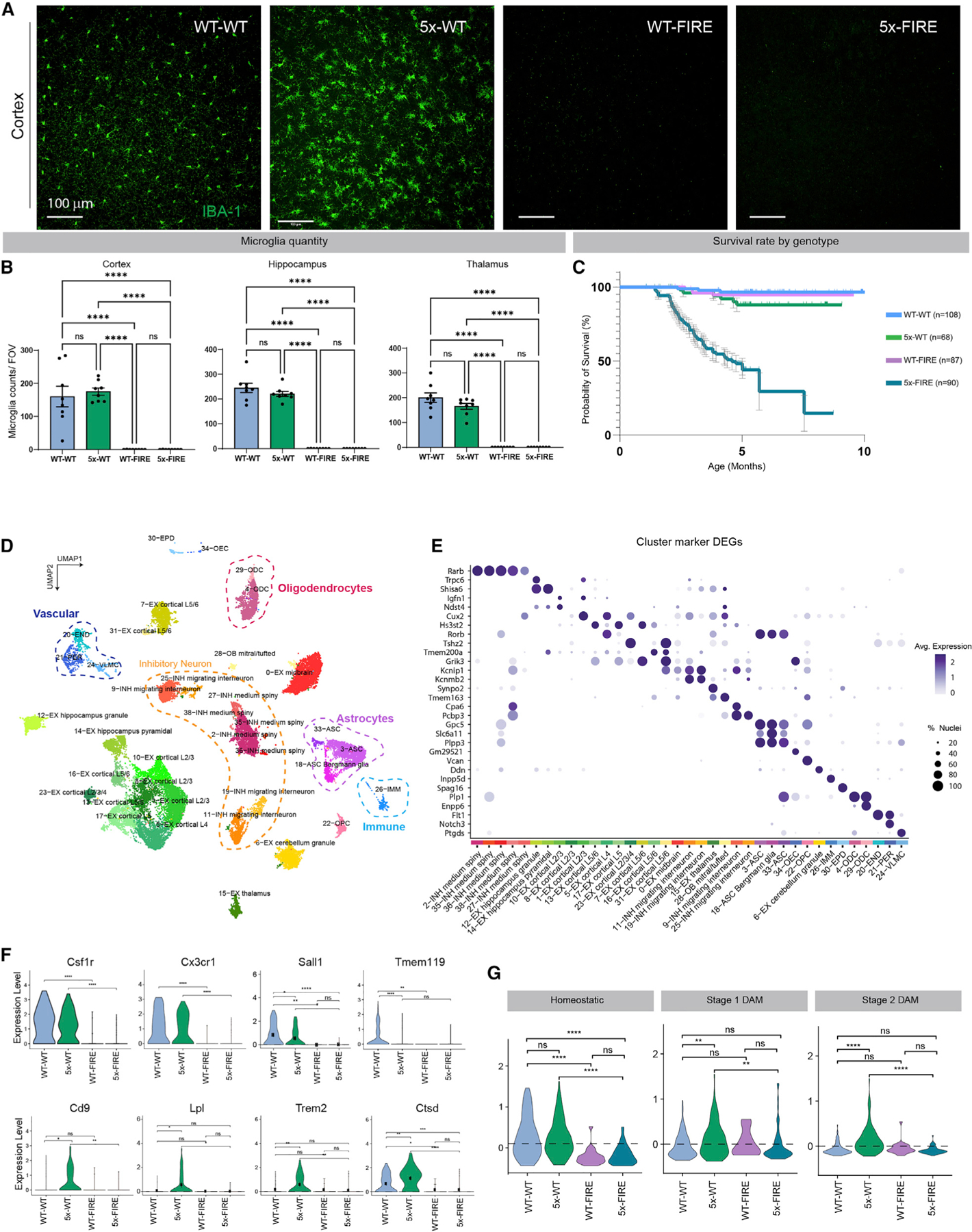
(A) Brains form 5–6-month-old mice (n = 8/group) were stained with IBA-1 (green). Representative confocal images from the cortex demonstrate a homeostatic distribution of IBA-1 immunoreactive microglia in WT-WT mice, a more activated clustering of microglia in 5x-WT mice, and absence of microglia in WT-FIRE and 5x-FIRE mice.
(B) FIRE mice lack microglia throughout the brain as quantified within the cortex, hippocampus, and thalamus.
(C) Kaplan-Meier survival analysis reveals early lethality in 5x-FIRE mice, with fewer than 29% of mice remaining alive at 6 months of age and only 15% remaining alive at 7.5 months. In contrast, WT-WT, 5x-WT, and WT-FIRE mice exhibit minimal lethality.
(D) Uniform manifold approximation and projection (UMAP) of snRNA-seq analysis of 5–6-month-old mice (n = 8/group) provides transcriptomic evidence of 37 distinct clusters, including multiple neuronal subtypes, several astrocyte and oligodendrocyte subtypes, and endothelial and immune cell clusters.
(E) A dot plot of the highest expressed gene for each cluster; size of dots indicates percent of cells expressing that gene; color indicates relative expression levels.
(F) The absence of microglia in WT-FIRE and 5x-FIRE mice is further confirmed by lack of CSF1R, CX3CR1, SALL1, and TMEM119 gene expression, among others. In addition, increased expression of several disease-associated microglial (DAM) transcripts, including CD9, LPL, TREM2, and CTSD, is observed within the 5x-WT group but not within 5x-FIRE mice.
(G) Whereas 5x-WT mice exhibit induction of both stage 1 and 2 DAM module genes, 5x-FIRE show no such induction. Scale bars, 100 µm in (A). All data presented as mean ± SEM. *p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01, ***p ≤ 0.001, ****p ≤ 0.0001.
