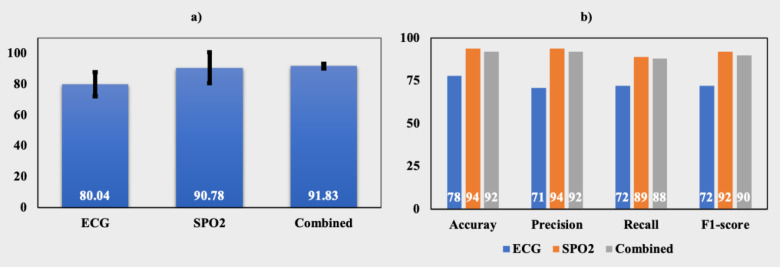
Figure 4:
a) accuracy (%) of the models after 10-fold cross-validation, b) accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score of all the models on the test data.
Figure 4-b) shows the performance of the models in the test set, which was separated during the train-test split. For each type of signal, a new model was created using the entire training set, and the performance of the model was evaluated by using accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score. Although the combined signal provided the best performing model from the cross-validation results, the SpO2-based model outperformed others in predicting the test set. It achieved the highest values of all the performance metrics. It had an accuracy of 94% whereas the ECG and combined signal provided accuracy of 92% and 78%, respectively and its prevision, recall, and F1-score were 94%, 89%, and 92%, respectively. As estimated from the validation result, the ECG-based model had the least values of the performance metrics. The combined signal-based model was the 2nd best model with accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score of 92%, 92%, 88%, and 90%.