FIGURE 4.
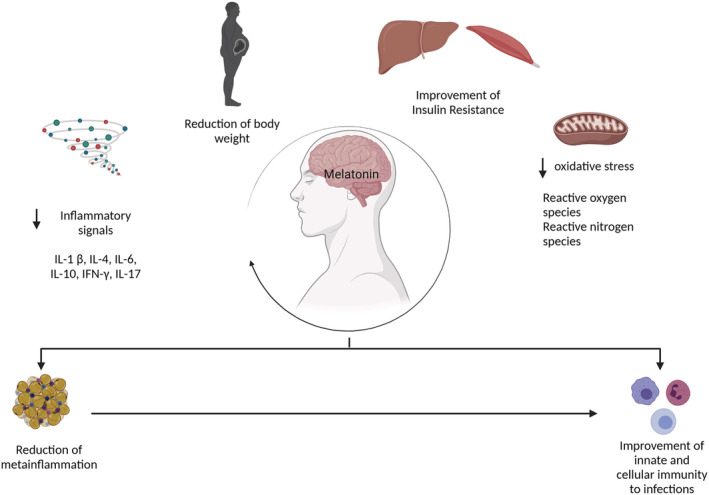
Possible mechanistic routes in which melatonin affects the infection process. Melatonin can reduce body weight and thus contributes to the reduction of visceral adipose tissue, which is the main source of inflammatory signals. In addition, melatonin has been reported to have antioxidant properties that reduce both reactive oxygen species (ROS) and nitrogen species. The reduction of low‐grade inflammation, along with antioxidant effects, contributes to an improved insulin resistance at both hepatic and muscle sites. All these mechanisms result in an improvement in both innate and cellular immunity to infections. Illustrations created with BioRender.com
