FIGURE 4.
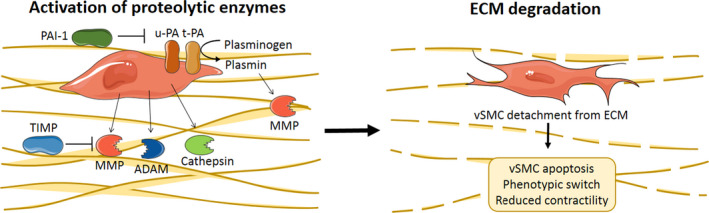
Extracellular matrix degradation by proteolytic enzymes regulated by vSMC. MMP, ADAM and cathepsins, activated and secreted by vSMC, can break down the ECM. Plasminogen can be activated into plasmin by u‐PA or t‐PA, both located on the vSMC membrane. PAI‐1 can inhibit u‐PA, and t‐PA. MMP can be inhibited by TIMP and activated by plasmin. ECM degradation causes vSMC detachment from the ECM and results in vSMC apoptosis, phenotypic switching and reduced contractility. Abbreviations: ADAM, the A disintegrin and metalloproteinase; ECM, extracellular matrix; MMP, matrix metalloprotease; PAI‐1, plasminogen activator inhibitor; TIMP, tissue inhibitors of matrix metalloproteinases; t‐PA, tissue‐type plasminogen activator; u‐PA, urokinase plasminogen activator; vSMC, vascular smooth muscle cell. Elements were modified from Servier Medical Art, licensed under a Creative Common Attribution 3.0 Generic License. https://smart.servier.com/; https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
