Figure 2.
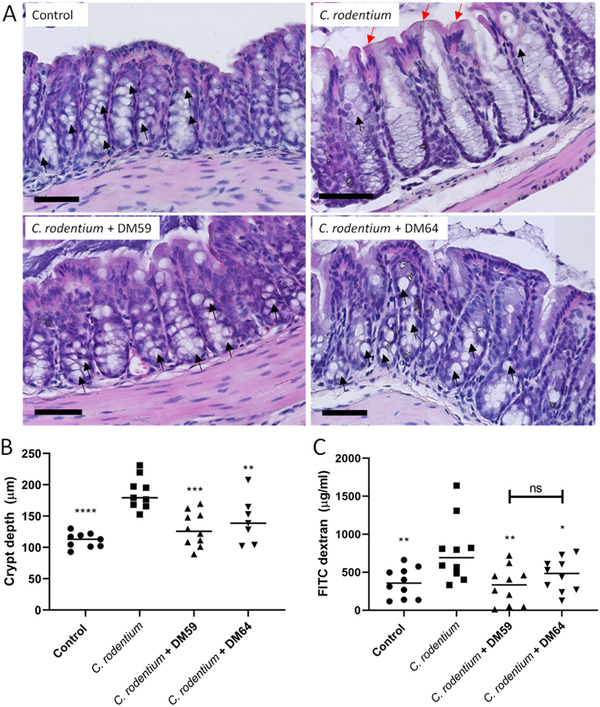
The protective impact of pectins on C. rodentium‐induced barrier disruption. Colon sections from mice were stained with H&E staining (A). From these sections, crypt depth was quantified to determine crypt hyperplasia (B). From plasma, FITC dextran flux was measured to determine intestinal permeability (C). Statistical differences between control and other experimental groups were determined using one‐way ANOVA, followed by Dunnet post‐test (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, and **** p < 0.0001). Black arrows indicate goblet cells and red arrows indicate epithelial damage. Scale bar = 70 µm.
