FIGURE 3.
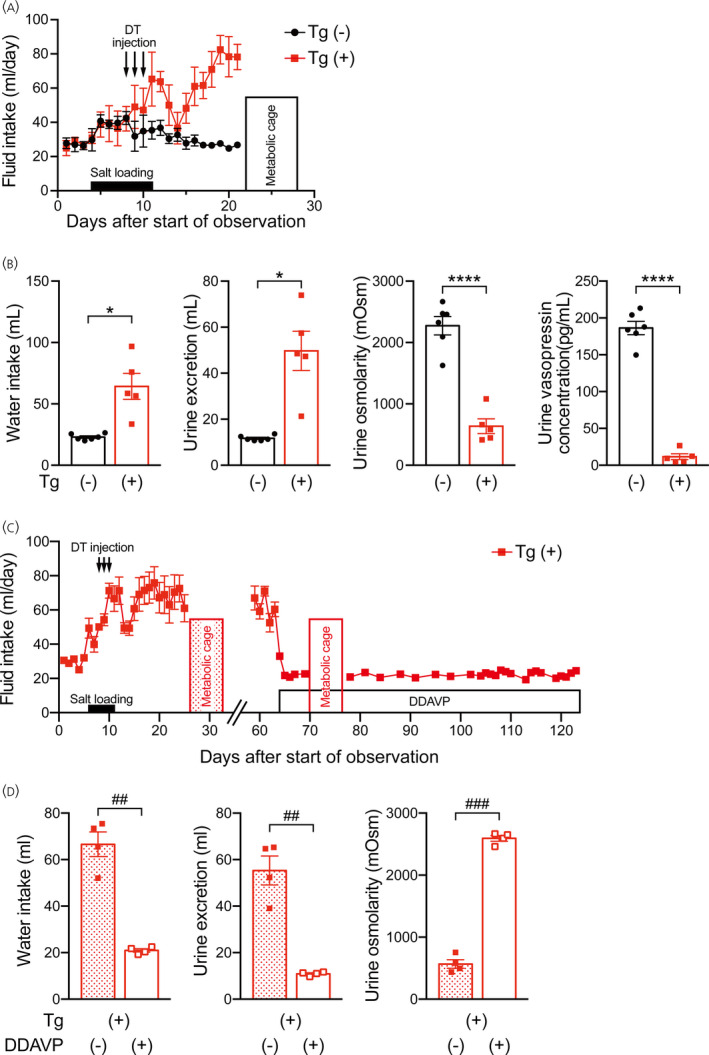
Effects of i.c.v. diphtheria toxin injection under the condition of salt loading on water intake, urine excretion, urine osmolarity and urine vasopressin concentration in transgenic rats. Diphtheria toxin (DT) was injected during the salt loading period. (A) Amounts of daily fluid intake in wild‐type (black) and transgenic (red) rats that received i.c.v. injections of diphtheria toxin under the condition of salt loading. (B) Amounts of water intake and urine excretion, urine osmolarity and urine vasopressin concentration in these rats during housing in metabolic cages. (C) Amounts of daily fluid intake in transgenic rats that received i.c.v. injections of diphtheria toxin under the condition of salt loading. The transgenic rats were treated with a vasopressin V2 receptor agonist (1‐desamino‐8‐d‐arginine‐vasopressin [DDAVP]) by an osmotic mini‐pump 8 weeks after injections of diphtheria toxin. (D) Amounts of water intake and urine excretion and urine osmolarity in these rats during housing in metabolic cages. n = 6 for wild‐type. n = 5 for transgenic rats (A, B) and n = 4 each for each group (C, D). *p < .05 and ****p < .0001 vs. wild‐type rats. ## p < .01 and ### p < .001, before vs. after treatment with DDAVP in transgenic rats. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM
