Fig. 3.
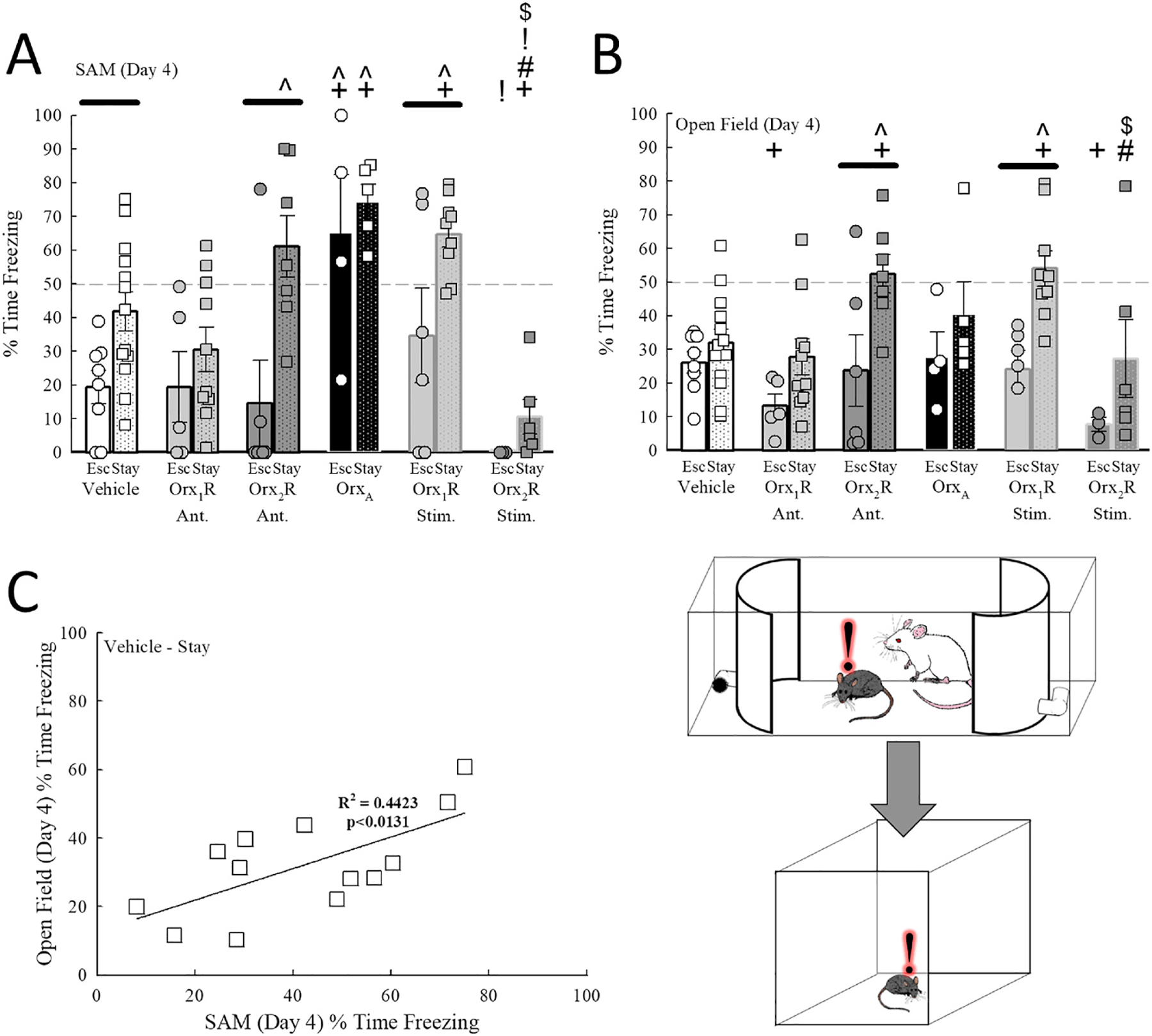
Socially induced freezing behavior in the SAM is transferred to the non-social OF Test in Stay mice. A) Stay mice treated with intra-BLA infusion of an Orx2R antagonist, but not an Orx1R antagonist, experience enhanced freezing in the SAM (Drug Effect, F5,70 = 9.6, p < 0.001; Phenotype Effect, F1,70 = 17.6, p < 0.001). Further, mice in OrxA and Orx1R stimulation groups exhibit enhanced freezing, while animals treated with an Orx2R agonist demonstrate significantly reduced freezing in the SAM. B) Antagonism of Orx1R receptors in the BLA reduced generalized OF Test freezing in Escape mice only, while Orx2R antagonist treatment increased OF freezing in Stay animals (Drug Effect, F5,70 = 3.3, p ≤ 0.011; Phenotype Effect, F1,70 = 21.4, p < 0.001). Additionally, freezing in the OF Test was increased in Orx1R stimulation group mice, while intra-BLA agonism of Orx2R reduced freezing in both phenotypes. C) In vehicle-treated control Stay mice, socially induced freezing in the SAM is positively correlated to OF Test freezing (F1,11 = 8.7, R2 = 0.4423, p ≤ 0.0131). −p ≤ 0.05 for comparisons between phenotypes in the same treatment group; +p ≤ 0.006 for comparisons to Vehicle-treated mice of the same phenotype; ^p ≤ 0.006 for comparisons to Orx1R Ant. group of the same phenotype; #p ≤ 0.006 for comparisons to Orx2R Ant. group of the same phenotype; !p ≤ 0.006 for comparisons to OrxA treatment animals of the same phenotype; $p ≤ 0.006 for comparisons to mice in the Orx1R stimulation group of the same phenotype.
