Figure 21.
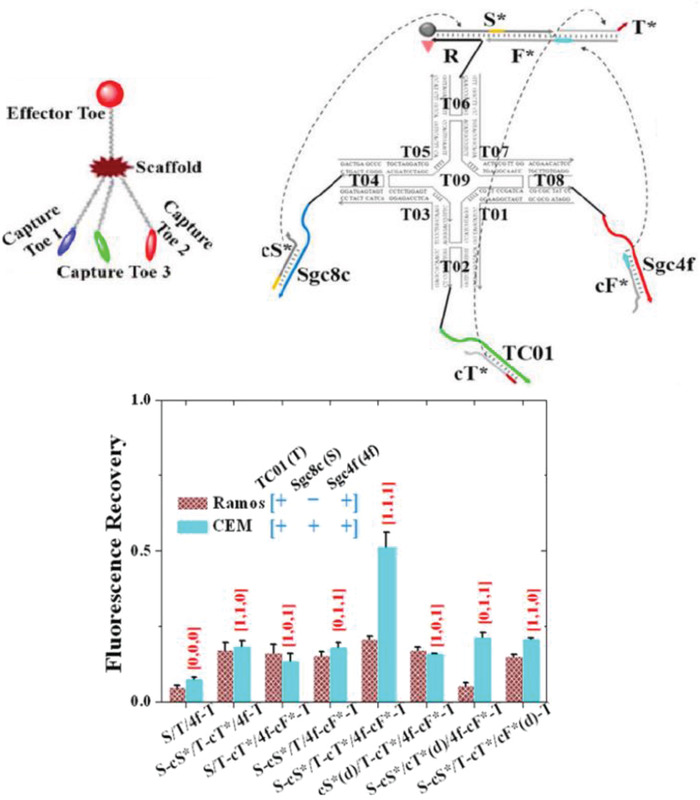
A three‐input DNA “nanoclaw.” Top: design and structure of the DNA nanoclaw. The nanoclaw contained three capture toes made of TC01, Sgc4f, and Sgc8c aptamers. In the presence of the correct cellular signals, the capture toes released barcode oligos (cT*, cF*, cS*, respectively) that interact with the effector toe and activate the nanoclaw for drug release or biosensing. Bottom: flow cytometry Cy5.5 fluorescence results of nanoclaw functionality against two cells (Ramos and CEM) that have known differences in cellular receptor makeup. X‐axis shows the various nanoclaw configurations tested, where X‐cX* indicates activation of a specific aptamer, cX*(d) represents a control in which the specific aptamer is inactivated by a fully complementary strand. X = S/T/4f. Reproduced with permission.154 Copyright 2014, American Chemical Society.
