Figure 2.
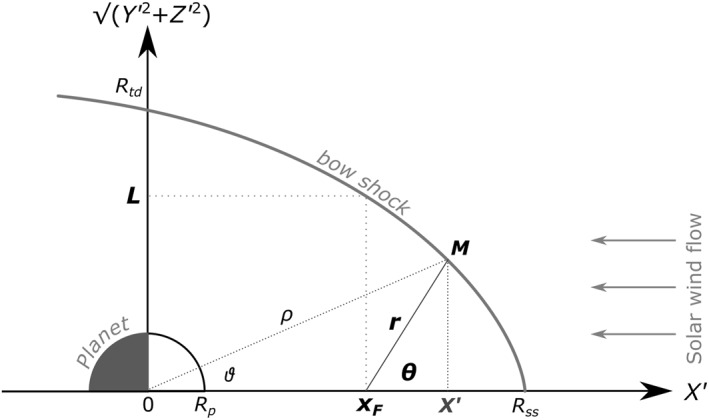
Typical 2D conic bow shock shape in the aberrated coordinate system. For a point M on the shock surface, ρ is the Euclidean distance to the shock from the center of the planet of radius R p, and r is the distance to the shock surface from the focus x F of the conic with semilatus rectum L and making an angle θ with the X′ direction, so that Equation (1) holds. ϑ is the usual polar angle, with respect to the center of Mars. R ss and R td are the standoff subsolar and terminator distances.
