Figure 1.
Identification of essential domains in Scc2
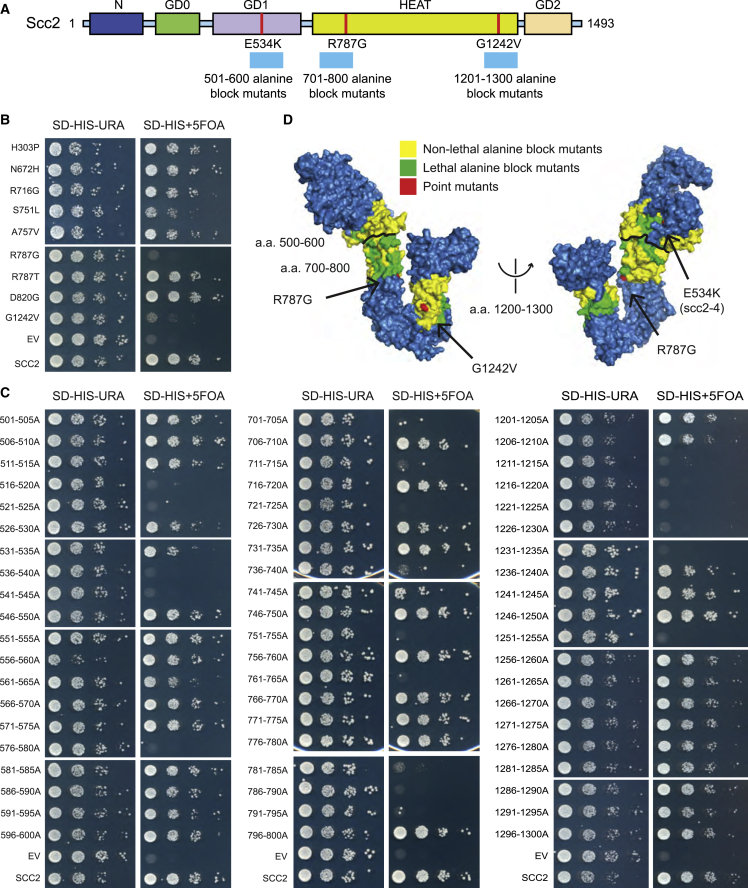
(A) Schematic of Ashbya gossipii Scc2 domains aligned to S. cerevisiae Scc2. Point mutants are indicated in red and cyan bars represent regions of the alanine block scan.
(B) Plasmid shuffle assay of CdLS mutations at residues conserved from Nipbl to Scc2. Endogenous SCC2 is deleted and covered by wild-type SCC2 on a URA3 selectable plasmid, whereas a second mutant copy of scc2 is present on a HIS3 selectable plasmid. 10-fold serial dilutions of the indicated strains were spotted on SD-HIS-URA and SD-HIS+5FOA. Growth on 5FOA indicates the viability of mutation. The R787G and G1242V mutations result in reduced growth.
(C) Identification of additional essential residues in Scc2 using the plasmid shuffle assay for alanine block mutants in Scc2.
(D) Mutated amino acids mapped to the C-terminal crystal structure surface map of Chaetomium thermophilum Scc2385–1840. Point mutants are indicated in red, lethal alanine block mutants in green, and non-lethal alanine block mutants in yellow.
See also Figure S1.