Figure 4.
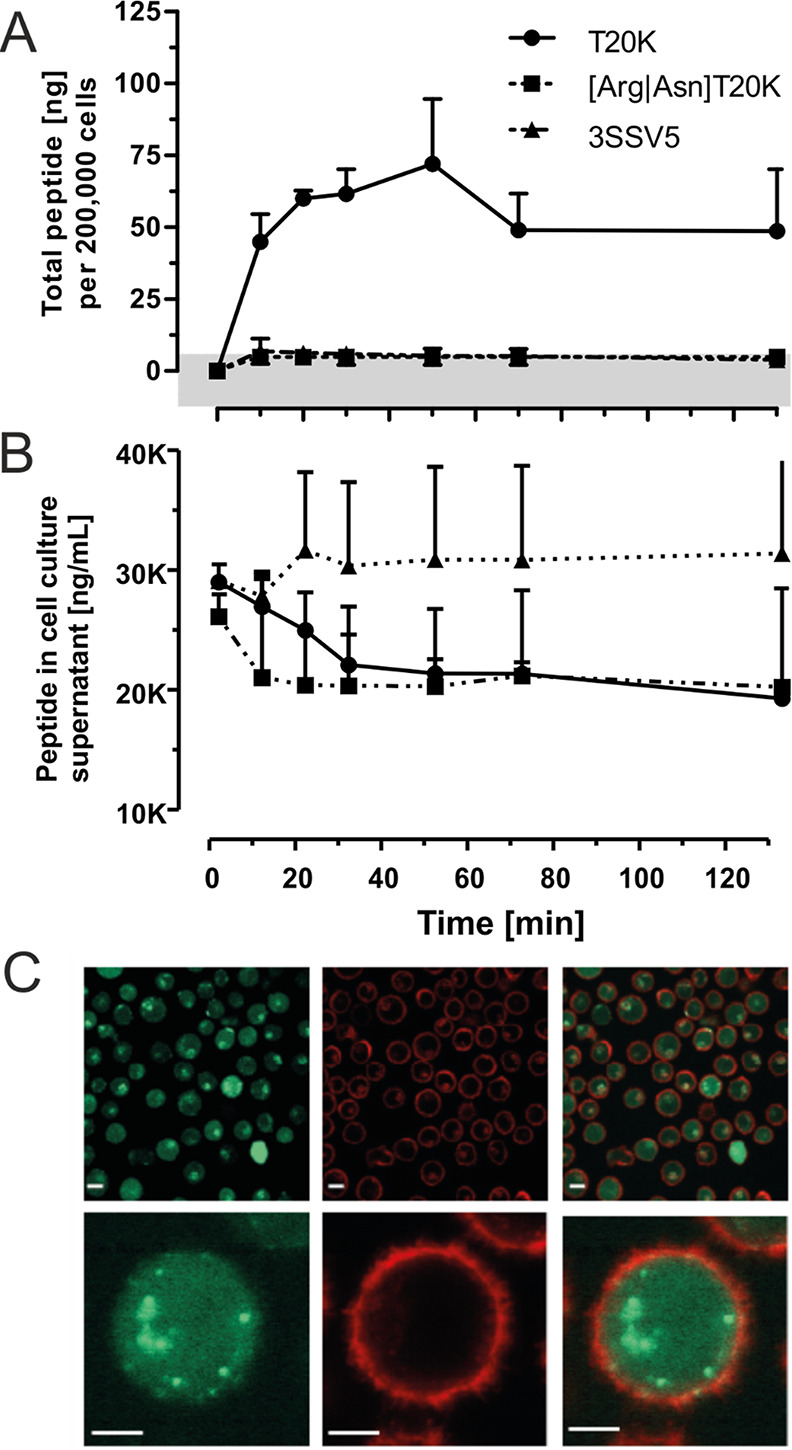
Cellular uptake of T20K into mammalian immune cells. Jurkat cells were incubated with native T20K as well as with 3SSV5 and linear T20K variants in a concentration of 10 μM (e.g., 21.17 μg/mL for the native species) in serum-free RPMI medium for various time points. The cell supernatant and cell pellet were harvested, and the peptides were extracted with acetonitrile. The lyophilized extracts were analyzed via LC–MS or HPLC-UV. (A) Whole cell extracts were analyzed with LC–MS to quantify analytes in absolute concentrations. The peptide levels determined for native T20K were in the nanogram range, whereas non-native peptide variants were not detected above the determined quantitation limit of 85 ng/mL (indicated by a grey horizontal bar). All data are provided as the mean of triplicates with standard deviation, except of the linear variant, which was analyzed two times. (B) The level of native T20K in cell supernatants revealed a decreasing trend overtime, which may account for the accumulation of the peptide in the cells. The levels of the other probes were not altered; both, the linear and the 3SSV5 variant remained at a constant level after a non-specific early sudden drop/rise, respectively. (C) Fluorescence microscopy images of Jurkat cells incubated with fluorescently tagged cyclotide T20K-CF. Jurkat cells were treated with 10 μM 5/6-carboxy-fluoresceine-tagged cyclotide (green) for 1 h at 37 °C and 5% CO2. Before measurements, cell membranes were visualized by a CellMask Orange (red) staining. Scale bars in the upper panel are 50 μm, and those in the lower are 5 μm.
