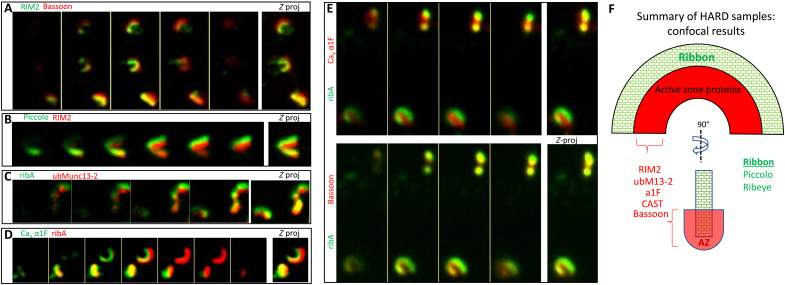
Fig. 3. HARD samples preserve the molecular architecture of rod ribbons at the level of confocal microscopy.
(A and B) RIM2 overlaps with the interior aspects of bassoon and piccolo. (C and D) Costained for ribA (anti–GP-Alexa488) and active zone proteins (anti–Rb-Alexa647): ubMunc13-2 or α1F (rabbit polyclonal). Here, the ribbon (ribeye) surrounds these AZ proteins. Images in (E) represent a triple, colabeling of ribA (anti–GP-Alexa488) versus α1F (anti–Rb-Alexa647) and bassoon (anti–Ms-Alexa546). Here, both α1F and bassoon are interior to the body of the ribbon (ribA), but the α1F signal overlaps less with ribeye than bassoon, which suggests that α1F is interior to bassoon. (F) Summary of active zone protein localizations, all of which were interior to the body of the rod ribbon (ribeye and piccolo) and determined in this study with HARD samples and confocal microscopy. Only RIM2 and α1F were analyzed in combination with bassoon, and they overlap with bassoon. CAST and ubMunc13-2 were only costained with ribeye; hence, their positions relative other AZ proteins were not assessed here.