FIGURE 4.
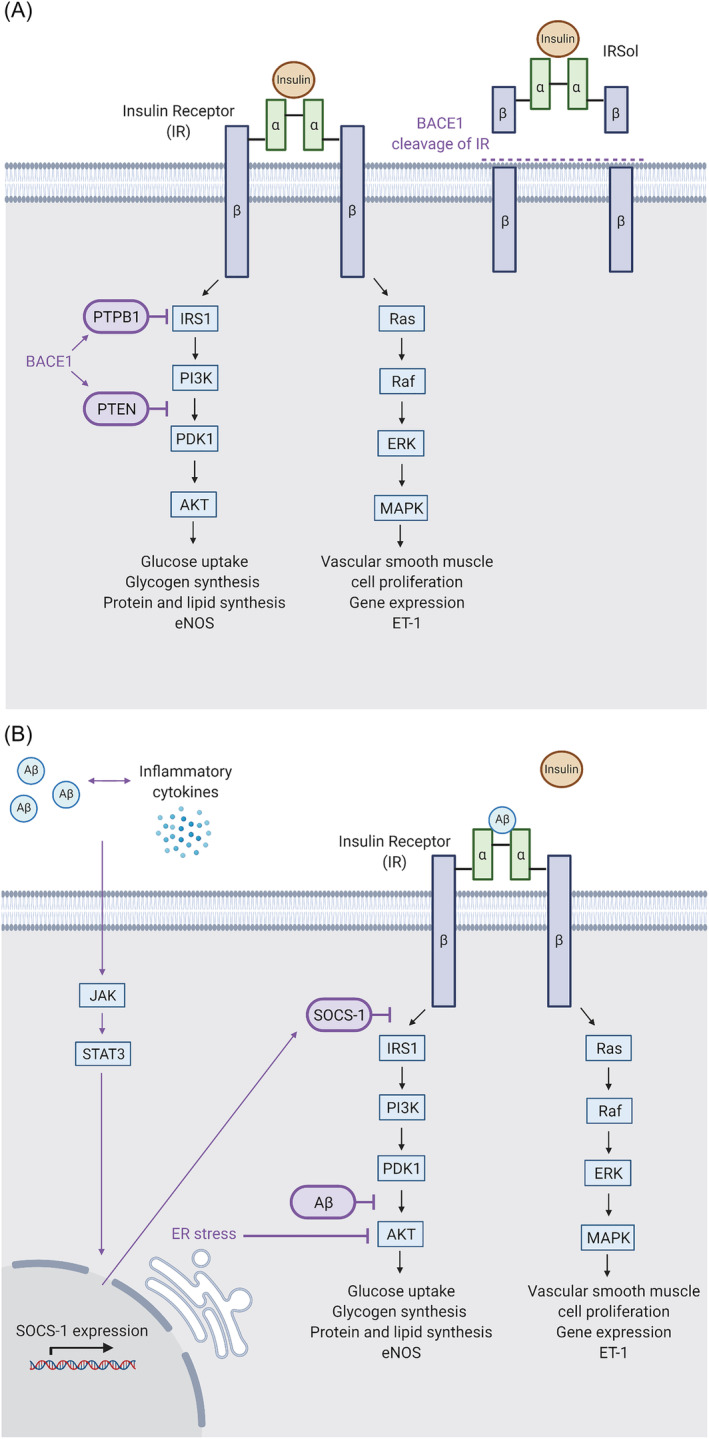
The role of BACE1 in the insulin signaling pathway. (A) BACE1 can impact insulin signaling through the negative regulators of the insulin signaling pathway, PTBP1 and PTEN (left), and through cleavage of the insulin receptor (IR) (right). PTBP1 and PTEN inhibit PI3K/Akt signaling affecting glucose uptake, glycogen synthesis, protein and lipid synthesis, and vasodilation. Cleavage of the insulin receptor prevents signaling in response to insulin binding. (B) BACE1‐mediated Aβ production can also impact insulin signaling. The accumulation of Aβ causes inflammation, which in turn stimulates the JAK/STAT3 signaling cascade, increased SOCS‐1 expression and inhibition of insulin signaling. PI3K/Akt signaling can also be inhibited by ER stress and Aβ mediated interruption of phosphoinositide‐dependent kinase‐1 (PDK) activity through binding with its target protein kinase B (PKB/Akt). Additionally, Aβ competitively binds the insulin receptor (IR) preventing insulin binding. Elevated BACE1 activity and Aβ can therefore lead to dysregulated insulin signaling. Created with BioRender.com
