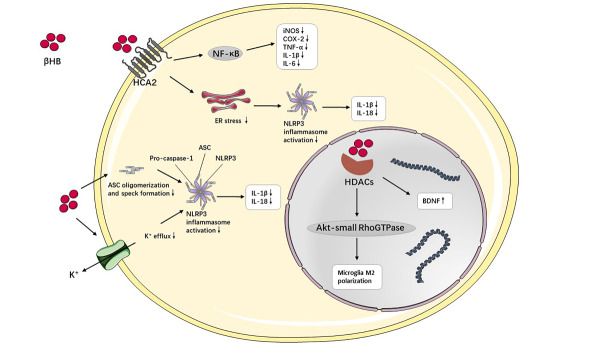
Figure 4.
The intracellular molecular mechanism of neuroinflammation mediated by beta-hydroxybutyric acid (βHB). βHB interacts with hydrocarboxylic acid receptor 2 (HCA2), nucleotide-binding domain-like receptor protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome and histone deacetylases (HDACs) directly or indirectly to exert anti-inflammatory effects. Abbreviations: ASC, apoptosis-associated speck-like protein with a caspase recruitment domain; BDNF, brain-derived neurotrophic factor; βHB, beta-hydroxybutyric acid; COX, cyclooxygenase; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; HCA2, hydrocarboxylic acid receptor 2; HDACs, histone deacetylases; IL, interleukin; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase; NF-κB, nuclear factor-κB; NLRP3, nucleotide-binding domain-like receptor protein 3; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α.