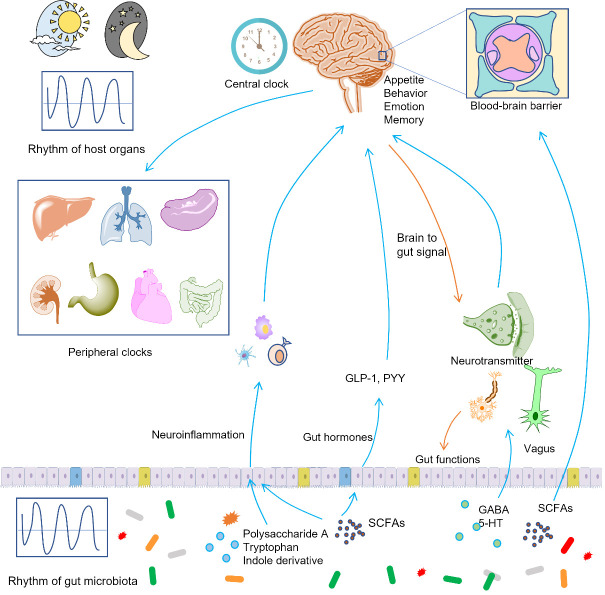
Figure 4.
Gut microbiota metabolites modulate the nervous system and circadian rhythm. Gut microbiota metabolites can modulate the cerebral inflammation, the production of gut hormones, the transmission of nervous impulse, the functions of blood-brain barrier to regulate the functions of brains such as the emotion and appetite. On the contrary, the brain can modulate the functions of gut such as the gut motility and secretion of digestive juice. The production of gut microbiota metabolites shows day-night rhythm, and this rhythm can be transported to the central clocks and peripheral clocks to modulate the systemic functions of hosts. Similarly, the central clock can transfer the light and dark cues to peripheral organs and gut microbiota, and thus synchronize the functions of gut microbiota and host clocks.