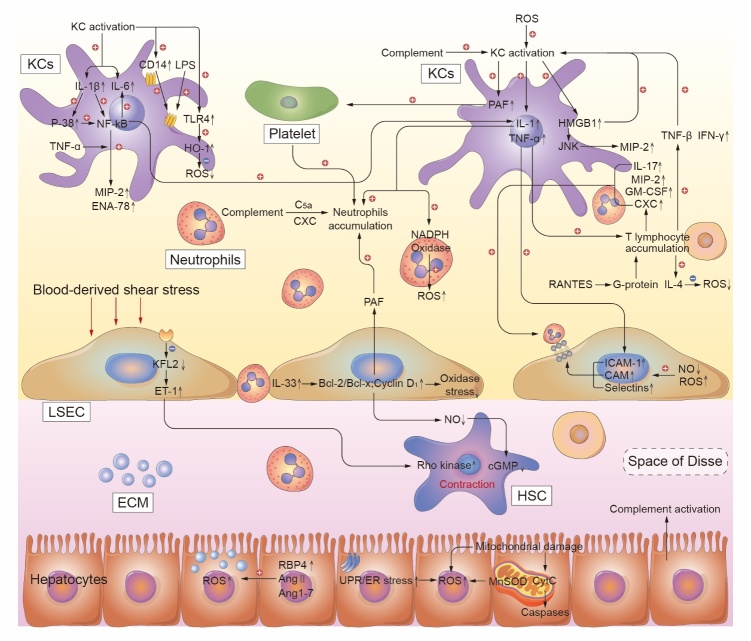
Figure 2.
The regulation of liver microenvironment components, including hepatic parenchymal cells, hepatic non-parenchymal cells (hepatic stellate cells, Kupffer cells, sinusoidal endothelial cells, neutrophils and lymphocytes), and extracellular matrix, during hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury. A summary of the specific molecular mechanisms regulating hepatocytes and interactions in the liver microenvironment are shown. LSEC, liver sinusoidal endothelial cell; HSC, hepatic stellate cell; KC, Kupffer cell; ROS, reactive oxygen species; ECM, extracellular matrix; IL-1, interleukin 1; IL-6, interleukin 6; IL-17, interleukin 17; IL-33, interleukin 33; IL-1β, interleukin 1β; HMGB1, high-mobility group box 1; IAC, inflammation associated cytokine; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor α; PAF, platelet activating factor; MIP-2, macrophage inflammatory protein 2; ENA-78, epithelial neutrophil activating protein 78; NF-κB, nuclear factor κB; TLR4, Toll like receptor 4; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; HO-1, heme oxygenase-1; RANTES, regulated upon activation normal T cell expressed and secreted factor; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; IFN-γ, interferon γ; GM-CSF, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor; ICAM-1, intercellular adhesion molecule-1; Bcl-2/Bcl-x, B cell lymphoma 2/x; TXA2, thromboxane; KFL2, kruppel like transcription factor 2; ET-1, endothelin 1; JNK, N terminal kinase; CAM, cell adhesion molecule; cGMP, cyclic guanosine monophosphate; RBP4, retinol binding protein; Ang 1-7, angiotensin 1-7; Ang Ⅱ, angiotensin Ⅱ; MnSOD, manganese containing superoxide dismutase; CytC, cytochrome C.