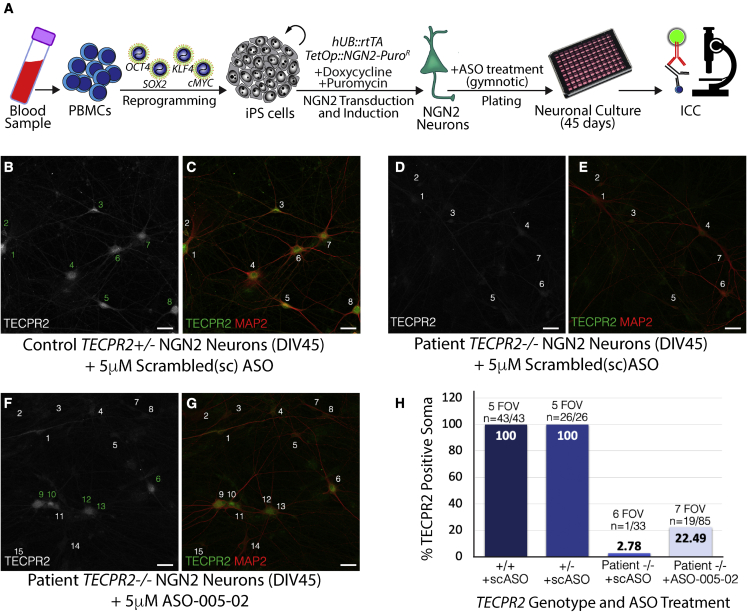
Figure 4.
ASO-005-02 can rescue TECPR2 protein expression in TECPR2-/- (SPG49) patient iPSC-derived neurons
(A) Generation of SPG49 patient iPSC lines and cortical excitatory neurons via reprogramming of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) with pluripotency factors (OCT4, SOX2, KLF4, and cMYC) and transcriptional programming with pro-neuronal factor NEUROGENIN-2 (NGN2). TECPR2-/- patient and TECPR2+/- control iPSC-derived neurons were treated with either 5 μM ASO-005-02 or a scrambled (non-targeting) negative control ASO during plating (single treatment, gymnotic delivery) and cultured for 45 days to allow neuronal maturation. Effect of ASO treatment on TECPR2 expression was assessed using immunocytochemistry. (B and C) Control TECPR2+/-; NGN2 neurons show clear TECPR2 immunoreactivity in soma and neuronal processes. (B) TECPR2 signal only and (C) a merge of TECPR2 (in green) with the pan-neuronal marker MAP2 (in red). Individual neurons in these panels are indicated (numbers 1–8). (D and E) SPG49 patient TECPR2-/- NGN2 neurons treated with scrambled (negative control) ASO do not show clear TECPR2 immunoreactivity. Individual neurons marked by MAP2 staining are indicated (numbers 1–7). (F and G) A subset of SPG49 patient TECPR2-/- NGN2 neurons treated with 5 μM lead ASO-005-02 show clear TECPR2 immunoreactivity, indicating rescue of TECPR2 protein expression in the form of TECPR2ΔEx8. These patient-derived neurons positive for TECPR2 signal are indicated by numbers in green in (F). (B–G) Scale bar, 20 μm. (H) Quantification of several FOVs indicates that ∼22.5% of SPG49 TECPR2-/- patient iPSC neurons exhibited rescue of TECPR2 protein expression in culture, after single treatment (gymnotic delivery) with lead ASO-005-02.