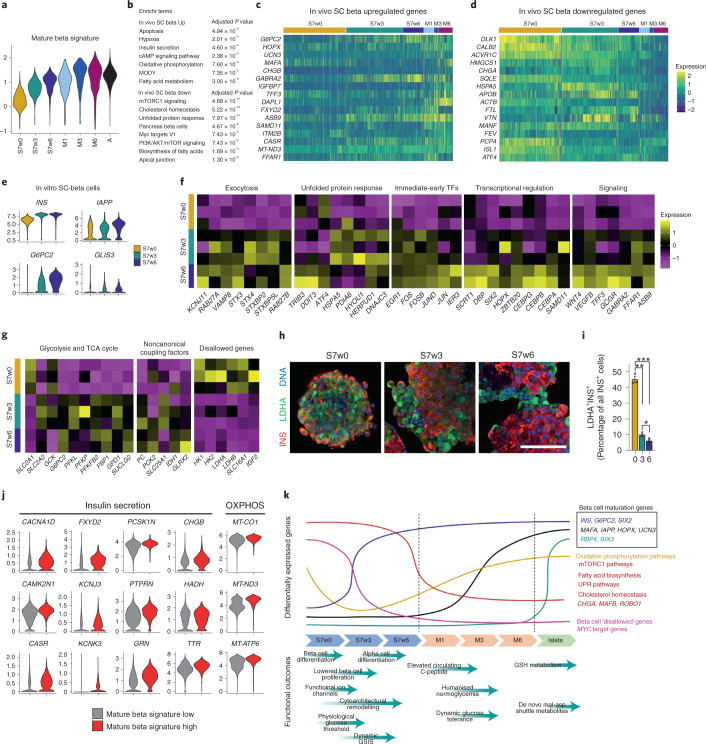
Fig. 6. Transcriptional maturation of stem-cell-derived beta cells.
a, Mature beta cell signature of SC-beta and adult beta cells from different times of origin. b, Gene sets enriched in the in vivo implanted SC-beta cells upregulated and downregulated genes compared with in vitro SC-beta cells. c, Expression of selected marker genes upregulated in the in vivo SC-beta cells. d, Expression of selected marker genes downregulated in the in vivo SC-beta cells. e, Violin plots representing the expression of mature beta cell markers in the SC-beta cells from S7w0, S7w3 and S7w6 times of origin. f, Average expression of genes associated with mature beta cell hallmark processes in individual SC-beta cell in vitro samples from different times of origin. g, Average expression of glucose metabolism, noncanonical coupling factors and disallowed genes in individual SC-beta cell in vitro samples from different times of origin. h, Immunostaining for disallowed gene LDHA protein and insulin (INS) of in vitro SC-islets from S7w0, S7w3 and S7w6 timepoints. Scale bar, 100 µm. i, Quantification of LDHA positive cells out of all INS positive cells in SC-islets from S7w0, S7w3 and S7w6. Data are presented as mean ± s.e.m. * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 One-way ANOVA with Welch’s correction; n = 3. j, Expression of genes associated with insulin secretion and oxidative phosphorylation in SC-beta cells with a high or low mature beta signature. k, Summary of functional and transcriptomic features of SC-islet maturation in vitro and in vivo.