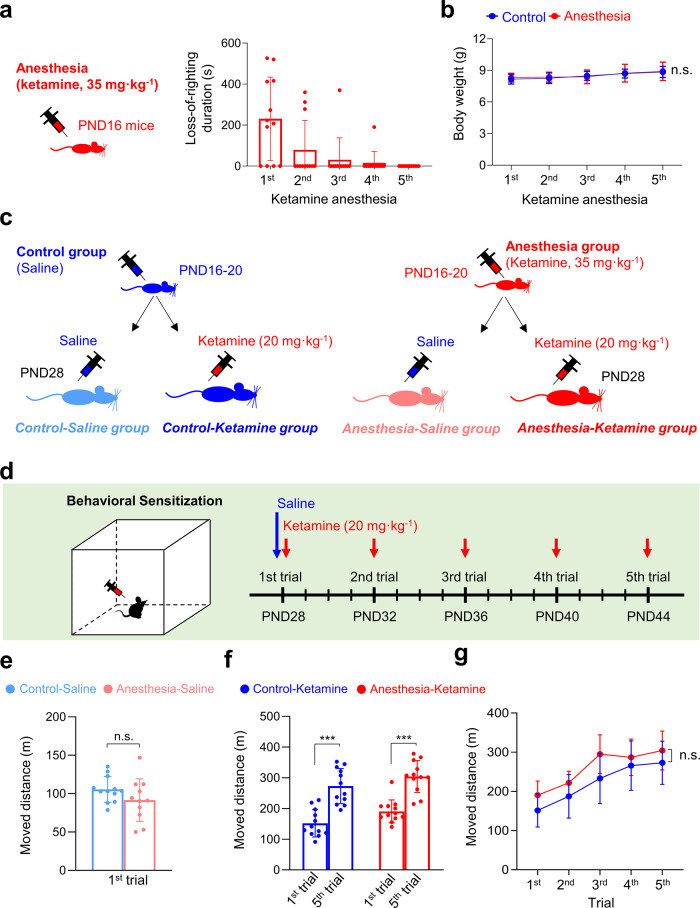
Fig. 1. Behavioral sensitization to low-dose ketamine is not affected in male mice that received early ketamine anesthesia.
a PND16 male mice were injected with an anesthetic dose of ketamine for 5 consecutive days. The duration of ketamine anesthesia, measured as the LOR reflex duration, was significantly reduced by repeated injections (acute tolerance) (p = 0.001, repeated measures [RM]-ANOVA; n = 12). b Normal weight gain in mice that received repetitive ketamine anesthesia (p = 0.115, RM-ANOVA; Control, n = 15; Anesthesia, n = 12). c–g Early repeated ketamine anesthesia does not affect the development of behavioral sensitization to low-dose ketamine. c, d Schematic diagram of the experimental design. A behavioral sensitization test was performed 1 week after anesthesia injections. e Early ketamine anesthesia did not affect baseline activity at PND28 (p = 0.158, Student’s t test; Control-Saline, n = 12; Anesthesia Saline, n = 11). f Behavioral sensitization to repeated low-dose ketamine developed in both groups (one-way ANOVA with Tukey multiple comparisons; Control-Ketamine, n = 12; anesthesia ketamine, n = 12). g The development of behavioral sensitization was comparable between the two groups (p = 0.583, RM-ANOVA; Control-Ketamine, n = 12; Anesthesia ketamine, n = 12). Values are presented as means ± SD (n.s., not significant; ***p < 0.001).