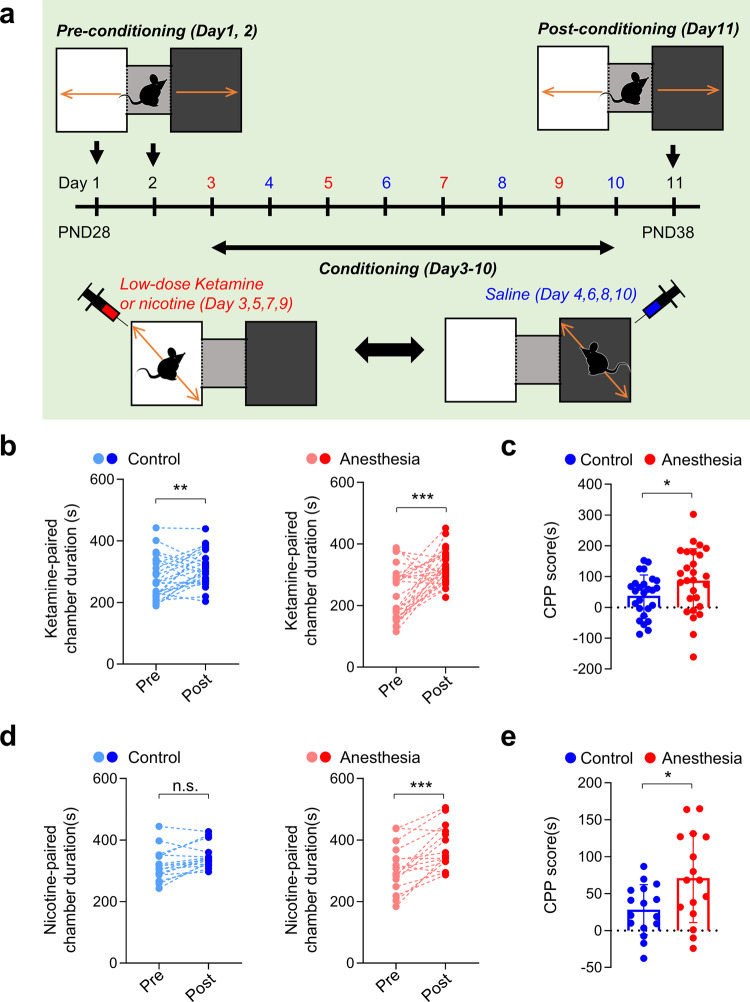
Fig. 2. Conditioned place preference for low-dose ketamine and nicotine are increased in male mice that received early ketamine anesthesia.
a–c Early repeated ketamine anesthesia increased low-dose ketamine-induced place preference 1 week after anesthesia injections (ketamine CPP). a Experimental scheme of ketamine CPP. b Time spent in the ketamine-paired (white) chamber was significantly increased after conditioning in both groups (Control, p = 0.007; paired t test; n = 26 mice; Anesthesia, p < 0.001; paired t test; n = 27 mice). c Summary graph comparing ketamine CPP scores between groups (p = 0.0496, Welch ANOVA; control, n = 26 mice; Anesthesia, n = 27 mice). d, e Early repeated ketamine anesthesia increased nicotine-induced place preference 1 week after anesthesia injections (nicotine-CPP). d Time spent in the ketamine-paired (white) chamber was significantly increased after conditioning in the Anesthesia group (p < 0.001) but not in the Control group (p = 0.056) (paired t test; control, n = 16 mice; Anesthesia, n = 16 mice). e Summary graph comparing nicotine-CPP scores between groups (p = 0.0192, Welch ANOVA; control, n = 16 mice; Anesthesia, n = 16 mice.). Values are presented as means ± SD (n.s., not significant; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001).