Fig. 2. Proposed implementation of the DSS structure with both the extrinsic and intrinsic planar chirality by transferring the BIC to q-BICs.
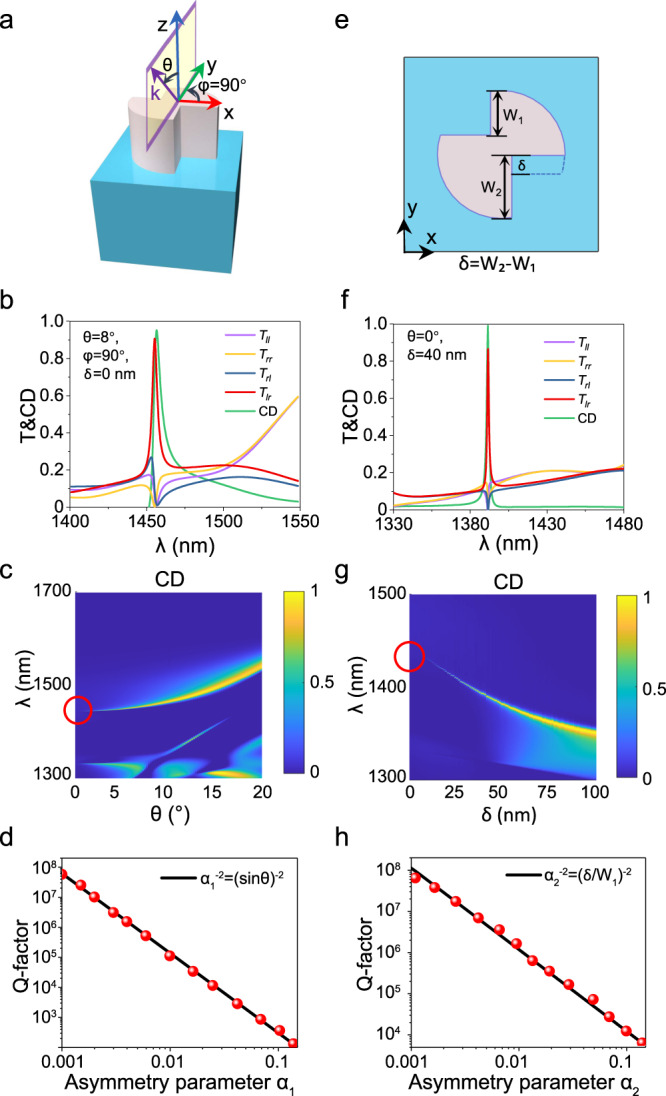
a, e Schematic of the symmetry-breaking processes that transfer the BIC to planar chiral q-BICs: (a) illumination symmetry breaking by varying incident angle θ, (e) in-plane geometry symmetry breaking by δ = W2-W1. b, f Simulated transmission Jones matrix spectra of Tll, Trr, Trl and Tlr as well as the CD spectrum of the metasurface with (b) the same parameters as Fig. 1d (δ = 0 nm) under oblique incidence (θ = 8°, φ = 90°) and with (f) an asymmetric structure parameter (δ = 40 nm) for normal incidences. c, g The evolution of CD spectra by continuous varying (c) incident angle θ along the φ = 90° direction and by (g) the geometry asymmetry parameter δ. d, h Dependence of the Q-factors of the planar chiral q-BIC mode on the relative asymmetry parameter (d) α1= sinθ, (h) α2= δ/W1 around the chiral q-BIC state. The solid line shows an inverse quadratic fitting.
