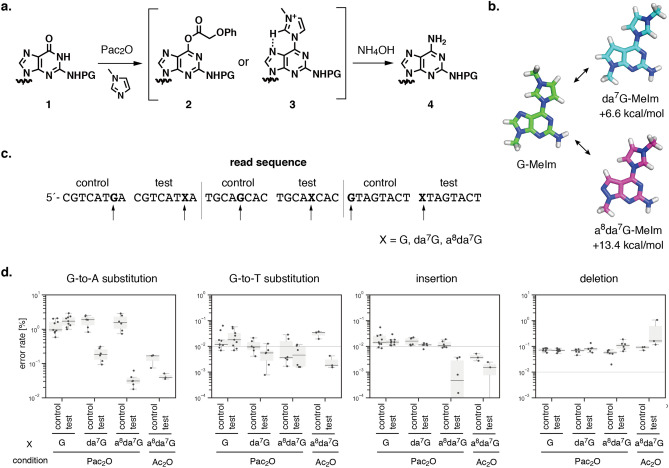
Figure 7.
Mechanism of G-to-A substitutions. (a) Previously proposed mechanism of diaminopurine formation, which is slightly modified based on this study19. (b) Optimized structure of the model of intermediates. (c) Positions of unnatural nucleosides. (d) Observed error rates related to deoxyguanosine. The synthetic conditions for Pac2O (n = 2) are 5-benzylthio-1H-tetrazole in anhydrous acetonitrile as an activator, phenoxyacetic anhydride in THF as a capping reagent A, 10% 1-methylimidazole in 10% pyridine-THF as a capping reagent B, 0.02 M I2 in THF/pyridine/H2O (90:<1:10, v/v/v) as an oxidation reagent, and 3% trichloroacetic acid in dichloromethane (TCA) as a deblocking reagent. The synthetic conditions for Ac2O (n = 1) are 1H-tetrazole in anhydrous acetonitrile as an activator, acetic anhydride in THF as a capping reagent A, 10% 1-methylimidazole in 10% pyridine-THF as a capping reagent B, 0.02 M I2 in THF/pyridine/H2O (90:<1:10, v/v/v) as an oxidation reagent, and 3% trichloroacetic acid in dichloromethane (TCA) as a deblocking reagent. Q5 High-Fidelity DNA polymerase was used for assembling reaction.