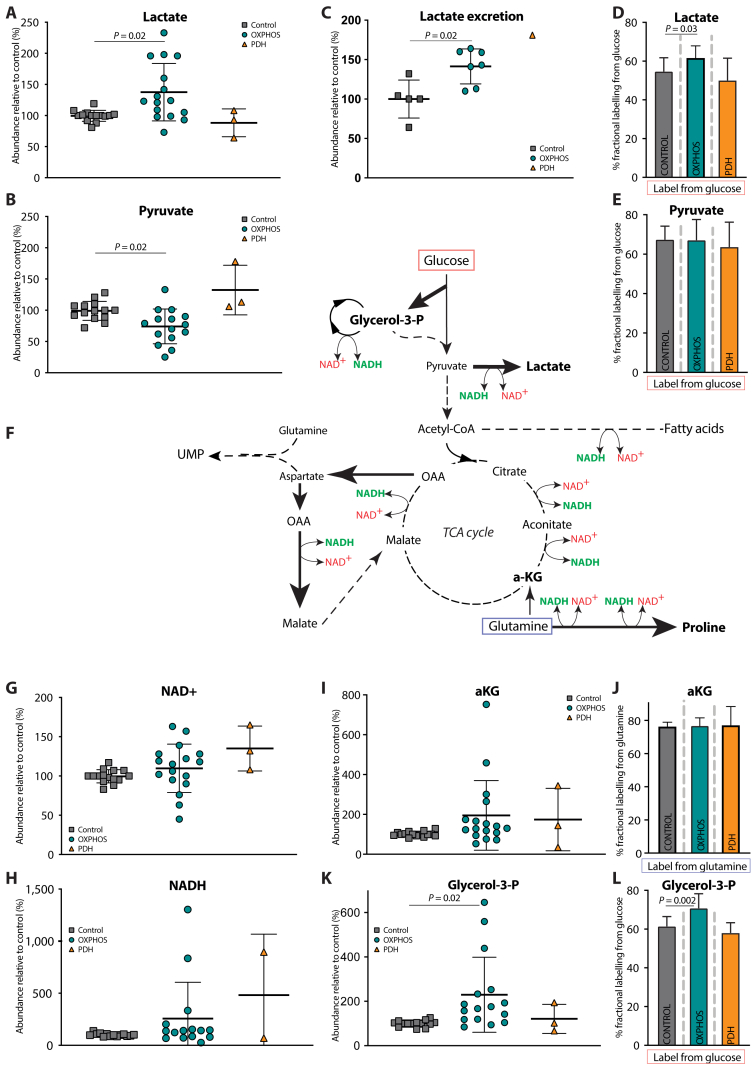
Figure 3.
Metabolic profile of OXPHOS dysfunction is linked to NAD+/NADH imbalance. A The relative intracellular abundances of lactate and B pyruvate in control, OXPHOS deficient and PDH deficient fibroblasts. C The relative excretion of lactate in medium in control (n = 5), OXPHOS deficient (n = 7) and PDH deficient (n = 1) fibroblast. D Fractional labelling in lactate and E pyruvate coming from U–13C glucose in control, OXPHOS deficient and PDH deficient fibroblasts. F Schematic representation of the central carbon metabolic reactions using NAD+/NADH as cofactors. Thickness of the arrows and the size of the metabolites indicate the magnitude of alteration in OXPHOS deficient fibroblasts compared to control. G The relative intracellular abundances of NAD+ and H NADH in control, OXPHOS deficient and PDH deficient fibroblasts. I The relative intracellular abundance of aKG and J the fractional labelling in aKG coming from U–13C glutamine in control, OXPHOS deficient and PDH deficient fibroblasts. K The relative intracellular abundance of Glycerol-3-P and L the fractional labelling in Glycerol-3-P coming from U–C glucose in control, OXPHOS deficient and PDH deficient fibroblasts. Unless otherwise specified, tracer metabolomics in control (n = 15), OXPHOS deficient (n = 17) and PDH deficient (n = 3) fibroblast cell lines (technical replicates 1–3 per cell line). Abundances normalized for protein content (BCA) and to the average of the controls per experiment. Statistics: one-way ANOVA with post-hoc Dunnett's T3 multiple comparison tests, and the error bars are +/−SD. a-KG: alpha-ketoglutarate; CoA: coenzyme A; Glycerol-3-P: glycerol-3-phosphate; OAA: oxaloacetate; OXPHOS: oxidative phosphorylation system; PDH: pyruvate dehydrogenase; TCA: tricarboxylic acid.