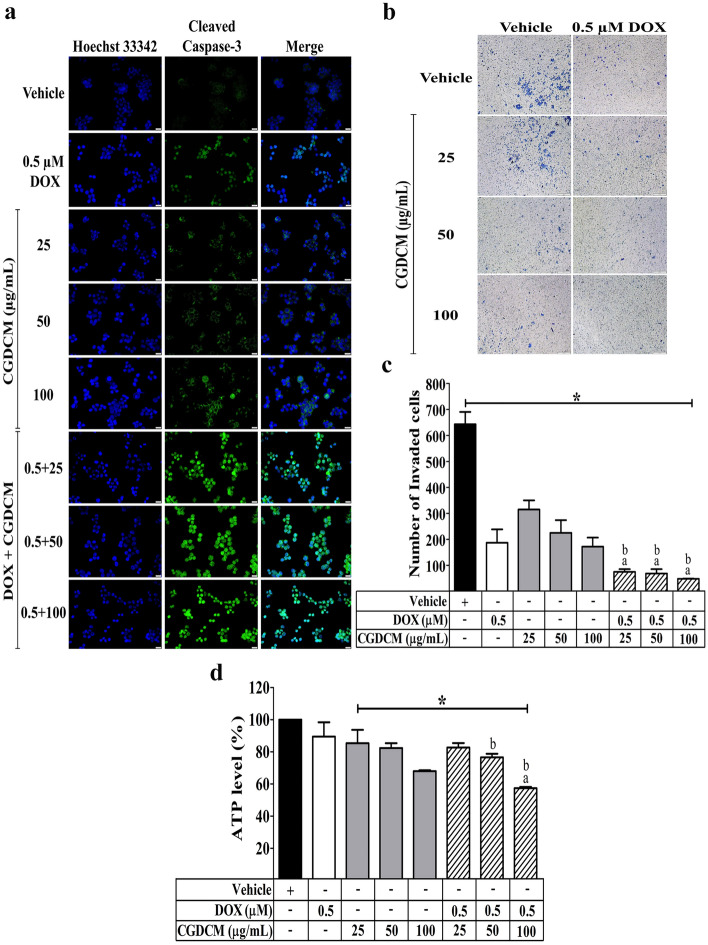
Figure 5.
The effect of CGDCM extract from stem bark of C. gigantea in the induction of apoptosis and in the inhibition of invasive activity in HepG2 cells treated with CGDCM (25, 50, and 100 µg/mL), DOX (0.5 μM), and combinations of the two for 24 h. (a) Representative images of apoptosis evaluated by the expression of cleaved caspase-3 with counterstained nuclei with Hoechst 33342 and visualized by fluorescence microscopy, bars = 20 µm. (b) Representative images of the anti-invasion effect evaluated by a Transwell assay and visualized under a light microscope, bars = 200 µm, and (c) histogram showing the total number of invading cells. (d) The production of ATP was expressed as a percentage compared with the vehicle control. Vehicle cells were treated with 0.8% DMSO. The data were analyzed using one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s HSD test and reported as the mean ± SD of three independent experiments (n = 3). *p < 0.05 compared to the vehicle group, a; p < 0.05 compared to the doxorubicin group, b; p < 0.05 compared to the treatment with CGDCM extract alone group. CGDCM, C. gigantea dichloromethane extract; DOX, doxorubicin.