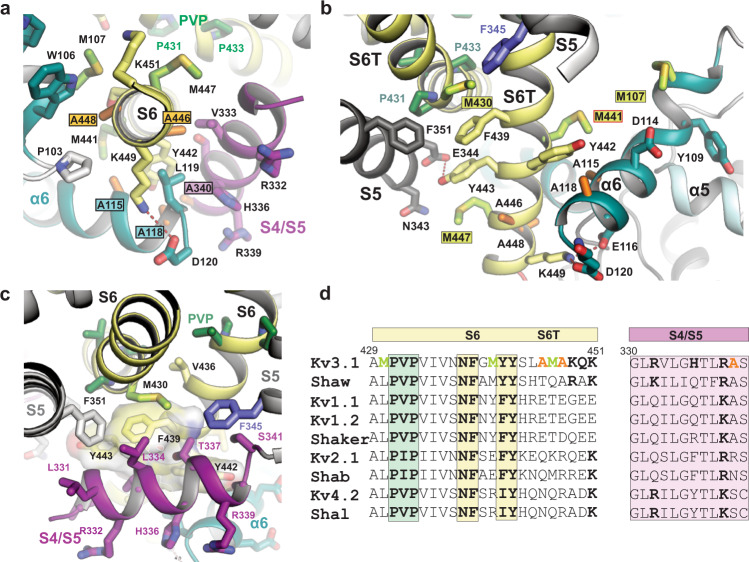
Fig. 5. A cluster of Kv3-specific alanines allows three-way interactions between α6, S4/S5 linker and S6T and location of Kv3.1-specific methionines in S6T.
a Cytoplasmic view onto S6T (pale yellow cartoon) of the lower gate in Kv3.1a, highlighting the close proximity to neighbouring helices S4/S5 and α6 of the T1 domain, which is possible due to the compact side chains of A115 and A118 (α6), A340 (S4/S5 linker) and A446 and A448 (S6T). The close contact allows the formation of a stabilizing salt bridge between D120 in α6 and K449 in S6T. b Rotated view from a, highlighting the abundance of Kv3-specific methionines in S6T (M430, M441, M447) and α6 (M107). S4/S5 linker is omitted for clarity. Red frame indicates the location variant M441L associated with EPM7. c Illustration of the hydrophobic surface created by aromatic S6T residues F439, Y442, and Y443 (displayed as semi-transparent surfaces) which cradles the S4/S5 linker (magenta) close to the PVP motif (green sticks) and the α6 helix in the T1 domain. F345 in S5 (slate blue) and M430 (lime green) from adjacent subunits form a sulfo-aromatic interaction. d Sequence alignment of the S6/S6T (left) and S4/S5 linker (right) regions of Kv3.1a with other T1-containing Kv channels (human or fruit fly). Kv3-specific alanines and methionines are highlighted in orange and lime, respectively. Conserved residues across other Kv families are shown in bold, including the PVP motif (green) and the aromatic S6T residues involved in electromechanical coupling interactions with the S4/S5 linker.