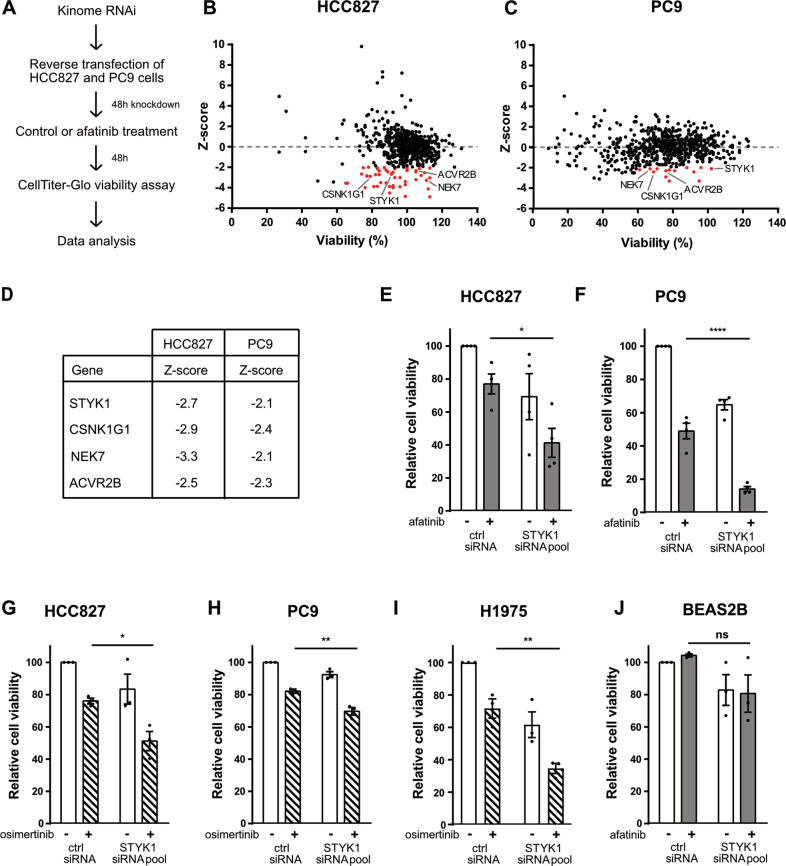
Fig. 1. STYK1 supports a prime mechanism of innate tolerance to afatinib in EGFR mutant NSCLC cells.
A Schematic representation of the kinome-wide RNAi screen. HCC827 and PC9 were reverse transfected with a custom-made siRNA kinome library and 48 hours post-transfection cells were treated with control (DMSO) or afatinib (1 nM or 5 nM for HCC827 or PC9, respectively). Cell viability was measured after an additional 48 h of incubation. B, C RNAi screen results in HCC827 (B) and PC9 (C) cells. siRNA pools with Z-scores < −2.00 and effects on viability >60% are indicated as red dots. D Common hit targets between HCC827 and PC9 with their respective Z-scores. E–J Cell viability analysis after reverse transfection of non-targeting control or STYK1 (pool) siRNAs treated for 48 h with control, afatinib or osimertinib. E HCC827 and F PC9 cells were treated with 1 nM and 5 nM afatinib, respectively. G HCC827 and H PC9 cells were treated with osimertinib (5 nM). I H1975 cells were treated with 10 nM osimertinib. J BEAS-2B cells were treated with 35 nM afatinib. Bars represent mean viability ± SEM. At least three independent experiments were performed.