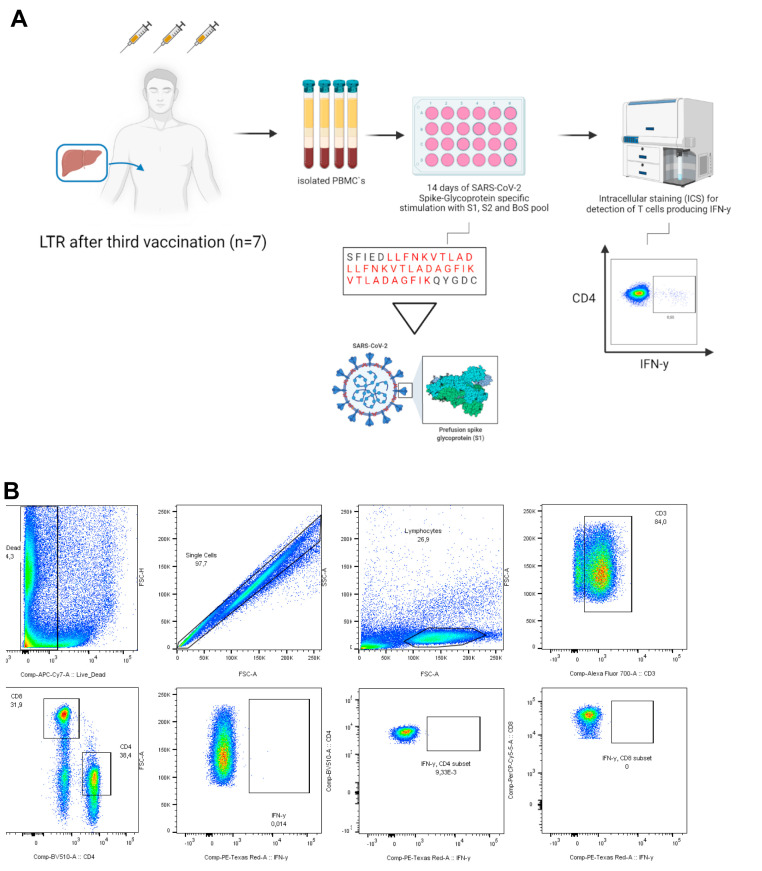
Supplementary Figure 1.
A, Methods and gating strategy of the in vitro T cell assay. B, To further evaluate T-cell response, in vitro clonal T-cell expansion was induced by stimulation a pool of 12 previously determined, highly immunogenic 15-mer peptides stemming from the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein (Supplementary Table 2) and anti-CD28/anti-CD49d antibodies (BD Bioscience, Franklin Lakes, NJ), 50 U/mL rIL-2 (Miltenyi Biotec, Bergisch-Gladbach, Germany) for 14 days. The pre-cultured cells were restimulated with the peptides (10 μg/mL) for 16 hours at 37 °C and 5% CO2. After 1 hour, Brefeldin A (5 μg/mL) was added to inhibit cytokine secretion. The cells were stained with Zombie NIR fixable viability dye (BioLegend, San Diego, CA) and the following fluorochrome-conjugated monoclonal antibodies cocktail: anti-CD3, clone UCHT1 (AlexaFluor700, BioLegend), anti-CD4, clone SK3 (BV510, BioLegend), anti-CD8, clone RPA-T8 (PerCP-Cy5.5, BioLegend), anti-CD14, clone 63D3 (APC-Cy7, BioLegend) and anti-CD19, clone HIB19 (APC-Cy7, BioLegend). For intracellular staining of IFN-γ (clone 4S.B3, PE-Dazzle594, BioLegend), cells were fixated and permeabilized using the Foxp3 transcription factor staining buffer set (eBioscience, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA). Cells were acquired on a BD fluorescence activated cell sorting Canto II or LSRFortessa II cytometer (BD Biosciences), and FlowJo version 10.8.0 (BD Biosciences) or FACSDiva V8 was used for the flow cytometric analysis.