Figure 1.
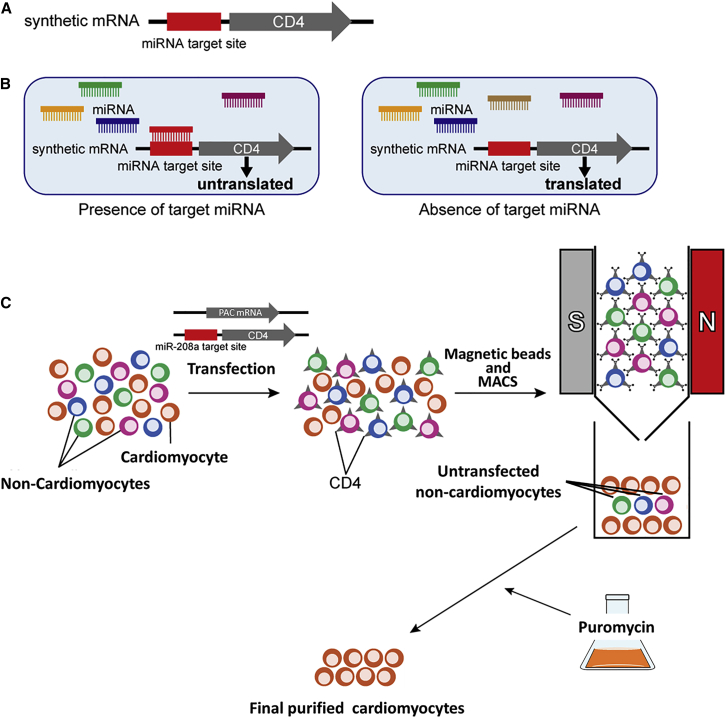
Schematic illustration of this study
(A) The miR-switch is synthetic mRNA made of two parts. One is the miRNA target site, which is a complementary sequence to the target miRNA, and the other is a protein coding sequence. In this study, CD4 was used as the protein for the selection marker in MACS.
(B) After the transfection of the miR-switch, if the cell expresses the target miRNA, translation from the miR-switch is inhibited, due to the interaction between the miRNA and the miR-switch. In contrast, if the cell does not express the target miRNA, the miR-switch is translated.
(C) Thus, upon transfecting miR-208a-CD4-switch to a heterogeneous cell population, CD4 translation is inhibited in CMs, but not in other cell types. Using CD4 microbeads and MACS, non-CMs bind to the MACS column, and CMs are isolated. By co-transfecting PAC mRNA, untransfected non-CMs are removed after puromycin administration.