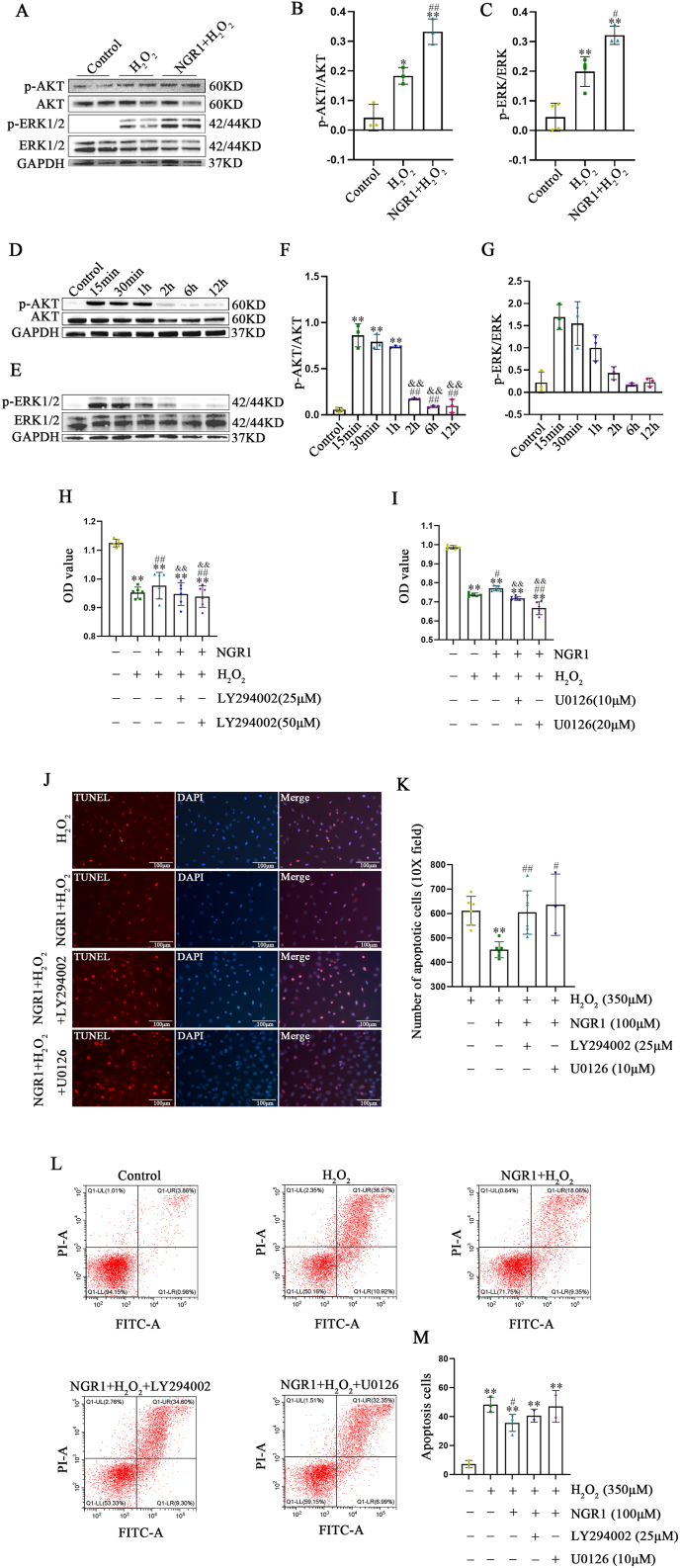
Fig. 11.
NGR1 protects H9C2 cells from H2O2-induced cell injury through the activation of PI3K/AKT and MAPK/ERK signaling pathways. Changes in intracellular p-AKT and p-ERK1/2 protein levels after treatment of H9C2 cells with 100 μM NGR1 and 350 μM H2O2 (A–C). *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 versus the control group; #P < 0.05 and ##P < 0.01 versus the H2O2 group. Changes in intracellular p-AKT and p-ERK levels at various time points in NGR1-treated H9C2 cells (D–G). **P < 0.01 versus the control group; ##P < 0.01 versus the 15 min group; &&P < 0.01 versus the 30 min group. The protective effect of NGR1 on H9C2 cells after the addition of signaling pathway inhibitors (H, I). **P < 0.01 versus the control group; #P < 0.05 and ##P < 0.01 versus the H2O2 group; &P < 0.05 and &&P < 0.01 versus the NGR1 + H2O2 group. TUNEL assay results for each group after the addition of LY294002 and U0126 (J, K). Scale bar: 100 μm **P < 0.01 versus the H2O2 group; #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01 versus the NGR1 + H2O2 group. Effect of Annexin V-PI flow-through assay LY294002 and U0126 on the protective effect of NGR1 (L, M). **P < 0.01 versus the H2O2 group; #P < 0.05 versus the NGR1 + H2O2 group.