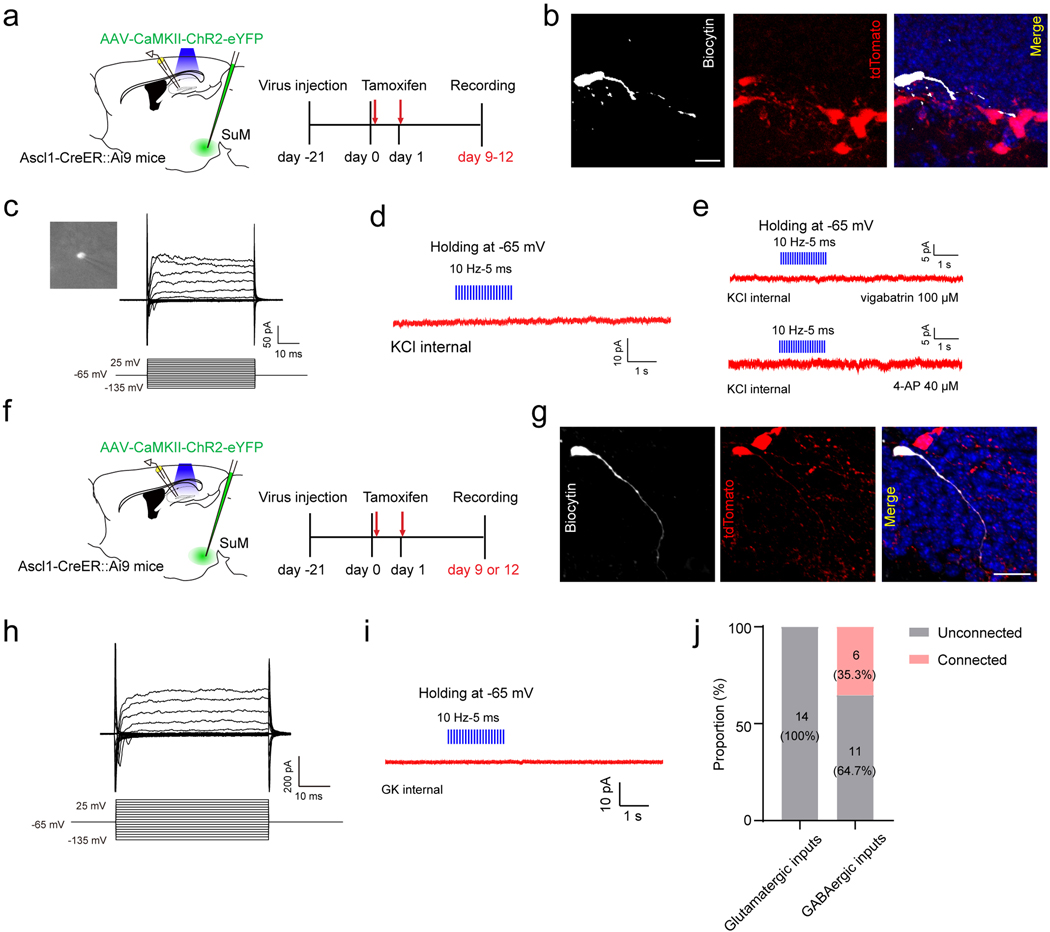
Extended Data Fig. 4. Electrophysiological recordings of adult-born neural progenitors or neuroblasts and immature neurons.
(a) Diagram of in vitro electrophysiological recording of progenitors/neuroblasts upon optogenetic stimulation of SuM-DG projections in Ascl1-Ai9 mice.
(b) Confocal images of a biocytin-labeled tdTomato+ cell at 9 dpi after whole-cell patch clamp recording. Scale bar = 20 µm.
(c) Electrophysiological characteristics of a neuroblast cell. Membrane currents from a non-responding cell were evoked by 50-ms voltage steps ranging from −135 mV to +25 mV at a holding potential of −65 mV.
(d–e) Light stimulation failed to induce any currents in 9 dpi tdTomato+ cells, with bathing 4-AP or vigabatrin (0 of 5 cells; Vh = −65 mV; KCl-based pipette solution).
(f) Diagram of in vitro electrophysiological recording of immature neurons at 9 or 12 dpi upon optogenetic stimulation of SuM-DG projections in Ascl1-Ai9 mice.
(g) Confocal images of a biocytin-labeled tdTomato+ cell at 12 dpi after whole-cell patch clamp recording. Scale bar = 20 µm.
(h) Electrophysiological characteristics of an immature cell at 12 dpi. Membrane currents from a non-responding cell were evoked by 50-ms voltage steps ranging from −135 mV to +25 mV at a holding potential of −65 mV.
(i) Light stimulation failed to induce any currents in 12 dpi tdTomato+ cells (0 of 14 cells; Vh = −65 mV; GK-based pipette solution).
(j) Proportion of connected and unconnected cells with the use of GK or KCl internal solution following blue light stimulation of SuM-DG projections. Numbers of cells are shown in parentheses.