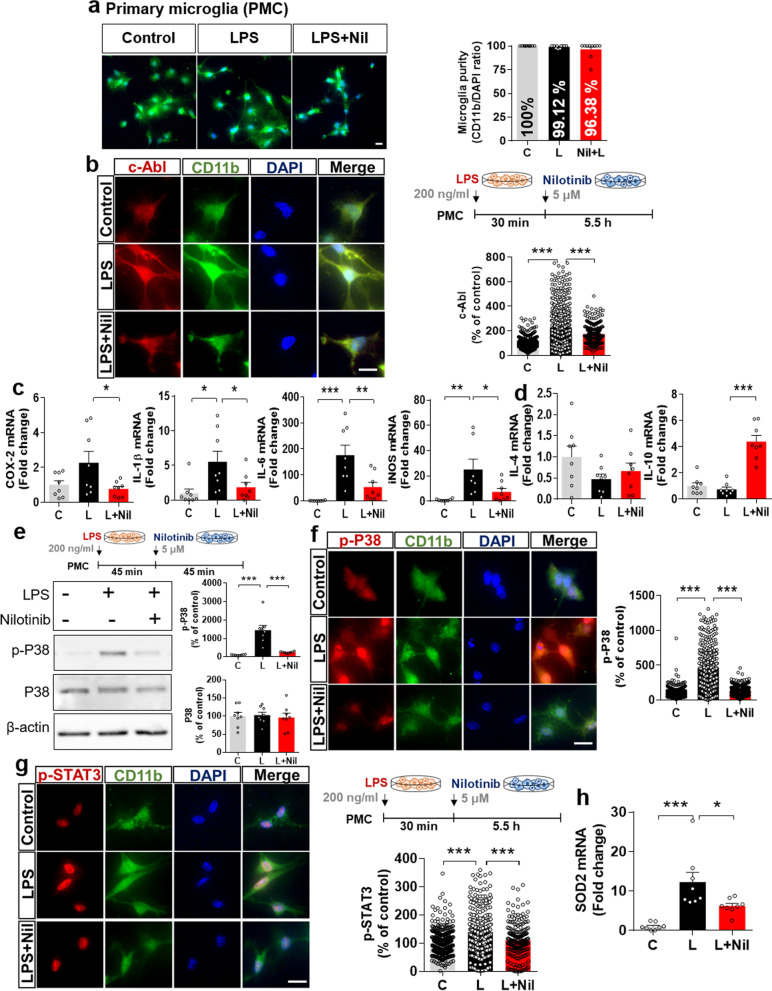
Fig. 4.
Nilotinib alters LPS-evoked changes in pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokine levels via P38/STAT signaling and suppresses Sod2 mRNA levels in primary microglia. a Assessment of primary microglial purity based on the CD11b/DAPI ratio (C: n = 371; L: n = 287; L + Nil: n = 216). b Immunocytochemistry analysis of c-Abl levels in LPS-treated primary microglia post-treated with nilotinib as shown (n = C: n = 561; L: n = 577; Nil + L: n = 298). c, d Real-time PCR analysis of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokine levels in LPS-treated primary microglia post-treated with nilotinib as shown (n = 8/group). e–g Western blotting analysis and immunohistochemistry staining of p-P38 and p-STAT3 levels in LPS-treated primary microglia post-treated with nilotinib as shown (p-P38 for western blot: n = 8/group; p-P38 for ICC: C: n = 526; L: n = 464; Nil + L: n = 352; p-STAT3 for ICC: C: n = 422; L: n = 358; Nil + L: n = 213). h Real-time PCR analysis of Sod2 mRNA in LPS-treated primary microglia post-treated with nilotinib (n = 8/group). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. Scale bar = 20 μM