Figure. 3. Co-treatment of MLT and AGP suppresses β-catenin signaling.
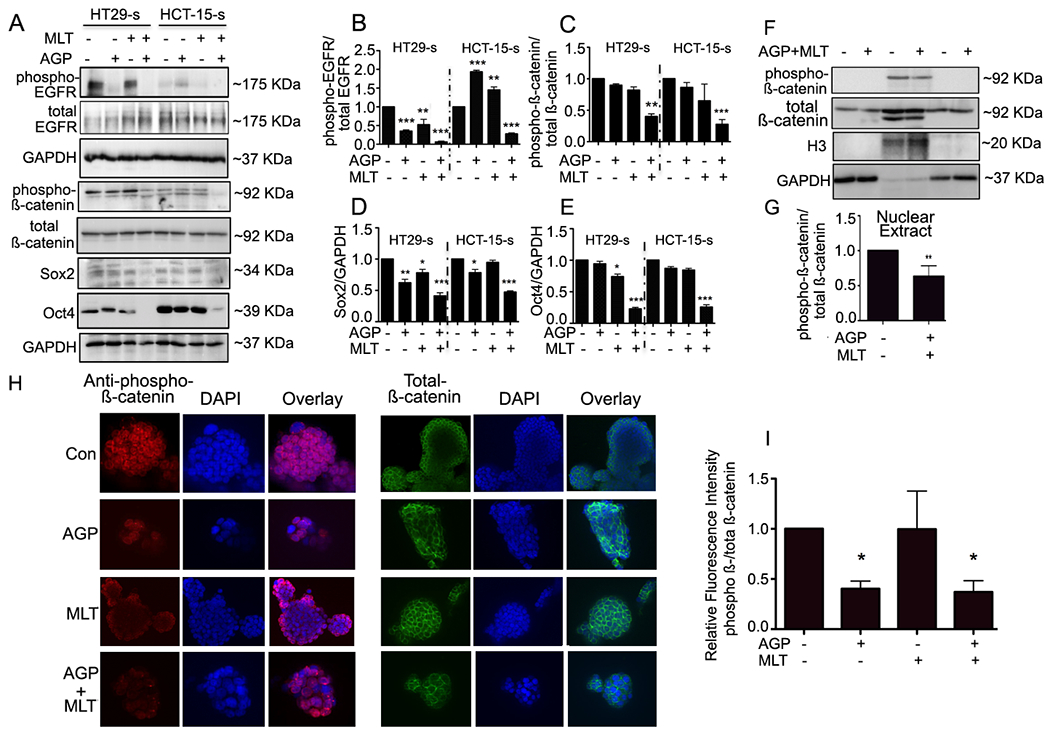
A. Immunoblots from treated or untreated CSCs extracts were used for monitoring β-catenin signaling protein expression. GAPDH was used as a loading control. Quantification of B. Phospho EGFR, C. Phospho β-catenin, D. Sox2, E. Oct4. Statistical significance was determined by one way-ANOVA followed by the Bonderroni test. (*P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001). F. HT29-s were grown on poly-L-Lysine coated coverslips. Phospho- (left panel)-and total β-catenin (right panel) protein expression were evaluated by confocal microscopy. Nuclei were stained using DAPI. Fluorescence intensity was determined and compared with untreated CSCs (G-H). I. Quantification. H. Analysis of phospho- and total β-catenin distribution. Equal number spheroids equivalents were electrophoresed and assayed by immunoblot. H3 and GAPDH levels served as the nuclear and cytoplasmic loading control, respectively. I. Representative quantification for phospho/total β-catenin using densitometry (**P<0.01).
