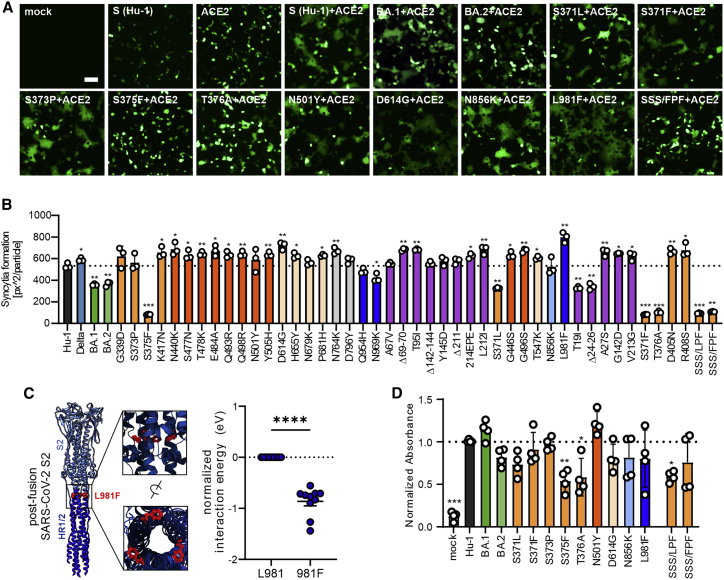
Figure 5.
Impact of mutations in Omicron Spike on cell-to-cell fusion and ACE2 interaction
(A) Representative fluorescence microscopy images of HEK293T cells expressing parental Hu-1 or indicated mutant S proteins, human ACE2, and GFP (green). Scale bar, 125 μm.
(B) Automatic quantification of syncytia formation of HEK293T cells expressing parental Hu-1 or indicated mutant S proteins and human ACE2. Bars represent the mean of three independent experiments (±SEM). Statistical significance was tested by two-tailed Student’s t test with Welch’s correction. ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.001.
(C) Overview on the SARS-CoV-2 post-fusion spike structure (downloaded from PDB: 6M3W) and comparative ReaxFF simulation of the mutation L981F.
(D) Binding of the indicated Hu-1 and mutant S proteins to ACE2 binding using whole-cell lysates of transfected HEK293T. Bars represent the mean of three independent experiments (±SEM). Statistical significance was tested by one-way ANOVA. ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.001.
See also Table S1.