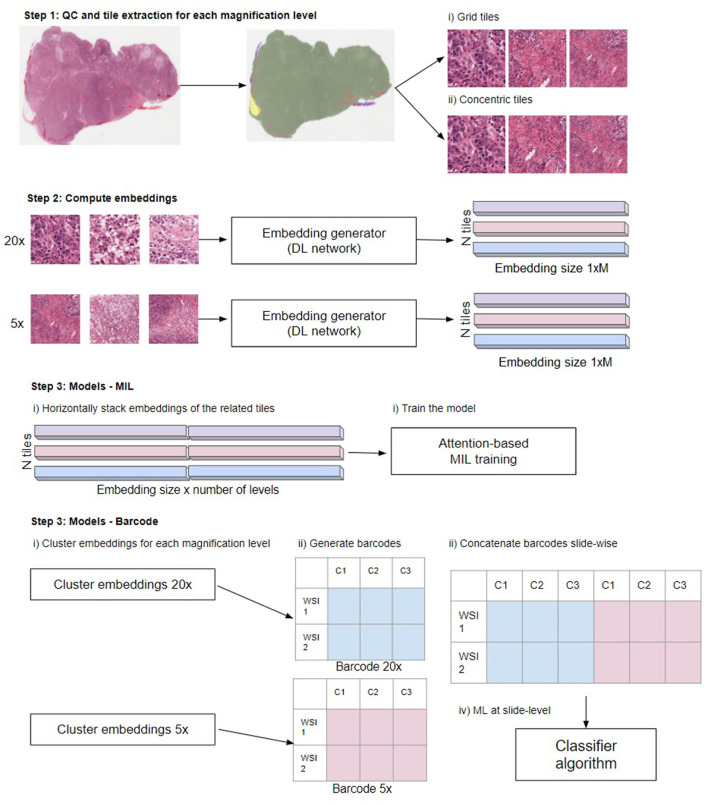
Figure 2.
Overview of the steps in the different multi-scale approaches used in this work. Step 1: Perform QC to extract in-focus tiles that contain tissue not covered by pen markers. Extract tiles for each magnification level using the grid and concentric approach. Step 2: Compute the embeddings from the tiles to obtain a 1xM representation for each tile, where M depends on the network (see main text “Compute embeddings”). Step 3, MIL: Train the model. Horizontally stack the embeddings of the related tiles. When using grid tiles, the same embedding at lower magnifications is duplicated and linked with different embeddings at higher magnification. Then, we provide the stacked embeddings as the input to the model. Step 3, barcode method: first cluster the embeddings for each magnification level. Subsequently, generate the barcodes (see reference 4 for details) and slide-wise concatenate the barcodes across magnifications. Finally, the thus created barcodes are used as input to a classifier: Illustration in Step 3 modified from Gueréndel et al. (4).