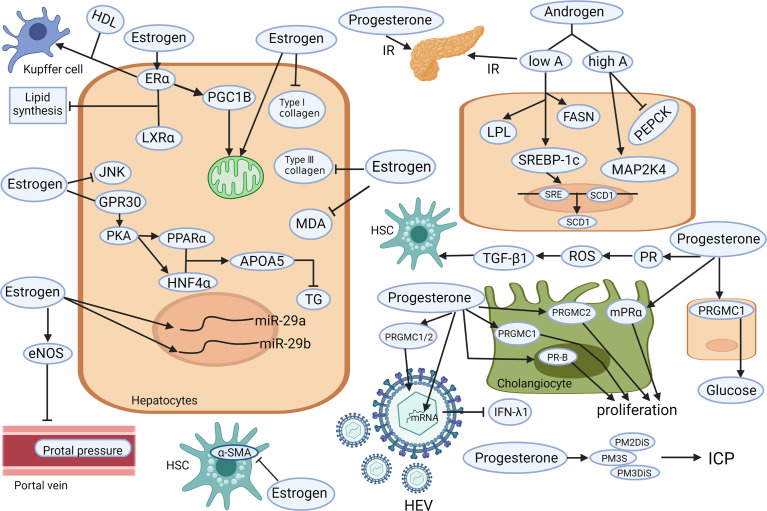
Figure 1.
Known mechanisms of the hepatoprotective and hepatotoxic effects of sex hormones (androgen, estrogen, and progesterone) on different liver cell types. Low level of testosterone increases the activity of LPL. The up-regulation of SREBP-1c and FASN lead to liver lipid deposition and aggravated insulin resistance. Those changes, together with the down-regulation of PEPCK and up-regulation of MAPK may lead to steatosis. Estrogen increases the content and oxidation capacity of mitochondria in hepatocytes. PGC1B promotes mitochondrial biogenesis. Estrogen also inhibits the activation of JNK and GPR30 to co-activate PKA and enhance liver PPARα and HNF4α to increase APOA5 expression and reduce TG. Estrogen (via its receptor alpha) induce cholesterol efflux from Kupffer cells with HDL. Estrogen can restore the expression of miR-29a/b to reduce the deposition of type I and III collagen, MDA, and α-SMA, to reduce liver fibrosis and other types of liver damage. Estrogen can also significantly reduce portal vein pressure by stimulating eNOS expression. Elevated progesterone leads to insulin resistance, stimulates PGRMC1 to increase hepatic glucose production, stimulates PGRMC1/2 to promote HEV replication, and inhibits IFN- λ1 expression. In addition, the accumulation of progesterone metabolites (PM2DiS, PM3S, PM3DiS) will increase the risk of ICP. Progesterone stimulates PR-B, PRGMC1, and PRGMC2 to facilitate bile duct cell proliferation. It also causes ROS environment via its receptor signaling, resulting in TGF-β1-activated HSC. APOA5, apolipoprotein A5; α-SMA, alpha-smooth muscle actin; eNOS, endothelial nitric oxide synthase 3; ERα, estrogen receptor alpha; FASN, fatty acid synthase; HDL, high-density lipoprotein; HSC, hepatic stellate cell; GPR30, G protein-coupled receptor 30; HNF4α, hepatocyte nuclear factor 4-alpha; ICP, Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy; IFN-λ1, type III interferon-λ1; JNK, Jun N-terminal kinase; LPL, lipoprotein lipase; IR, insulin resistance; LXRα, liver X receptor alpha; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; MDA, malondialdehyde; mPRα, membrane progestin receptor alpha; PEPCK, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase; PGC1B, proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1B; PGRMC, progesterone receptor membrane component; PKA, protein kinase A; PM2DiS/PM3DiS/PM3S, progesterone metabolites; PPARα, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha; PR, progesterone receptor; ROS, reactive oxygen species; SCD1, stearoyl-CoA desaturase1; SRE, sterol regulatory element; SREBP-1c, sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1c; TG, triglyceride; TGF, transforming growth factor (Created with Biorender.com with a publication license).