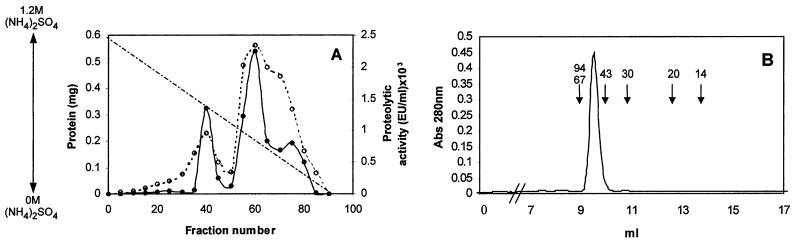
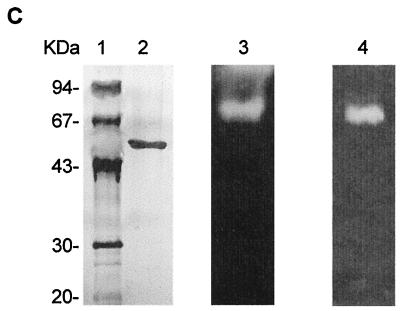
FIG. 1.
Chromatography steps and SDS-PAGE used for purification of calcium-dependent protease Fpp1 from F. psychrophilum. (A) Phenyl-Sepharose chromatography profile. The active unbound fraction from DEAE-Sephacel chromatography was applied to a Phenyl-Sepharose column in 1.2 M ammonium sulfate. The samples were eluted with a linear 1.2 to 0 M ammonium sulfate gradient (dashed line). Fractions were collected and assayed to determine caseinolytic activity (dotted line) and protein content (solid line) as described in Materials and Methods. (B) Elution pattern for Fpp1 protease with FPLC Superdex 75 gel filtration chromatography. A concentrated solution containing the proteolytic activity recovered during Phenyl-Sepharose column stepwise elution was loaded onto a Superdex 75 FPLC gel filtration column and chromatographed as described in Materials and Methods. The positions of molecular mass markers (in kilodaltons) are indicated by arrows. Abs 280 nm, absorbance at 280 nm. (C) SDS–12.5% PAGE of the purified calcium-dependent Fpp1 protease. The positions of molecular mass markers (in kilodaltons) are indicated on the left. Lane 1, molecular mass markers; lane 2, silver-stained purified Fpp1 (0.8 μg); lanes 3 and 4, caseinolytic and gelatinolytic activities of purified Fpp1 as determined by substrate gel electrophoresis with 1% sodium caseinate and gelatin, respectively, as described in Materials and Methods.