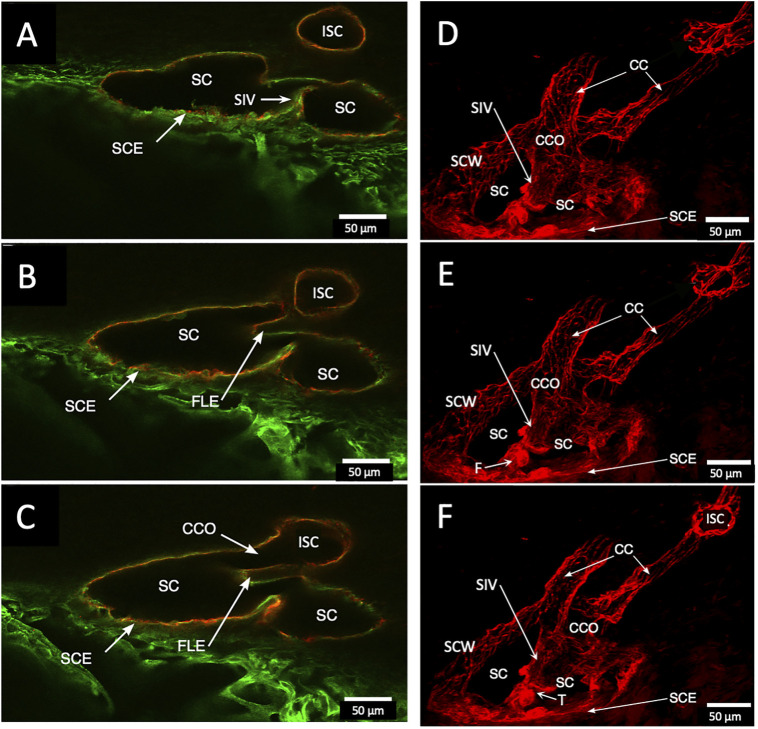
FIGURE 5.
Schlemm’s canal inner and outer wall connections—conduits lined by the endothelium and basement membrane labels in two different specimens. (A–C) Merged CD31 (red) and Col type 4 (green) confocal images. Schlemm’s canal (SC), SC endothelium (SCE), collector channels (CCs), collector channel ostia (CCO), and relationship to flap-like extensions (FLE) are apparent. The funnel-shaped structure (F) develops into a cylindrical configuration to create a SC inner wall valve-like conduit (SIV) extending from SCE across SC to an FLE at a CCO. The FLE originates from the external wall sclera with a hinged arrangement forming one wall of a CCO. Notably, the cylindrical structure spanning SC approaches the external wall at the location where the CCO forms. (D–F) New specimen with confocal projection, following CD 31 labeling, outlines vascular conduits, including an SIV arising from SCE, to join collector channels passing to more distal intrascleral channels. (F) CC exits SC and travels distally to join an intrascleral channel (ISC), which runs circumferentially. T is a localized artifactual disruption of SIV continuity. (A–C) #37LSN715; (D–F) #20RIN8.