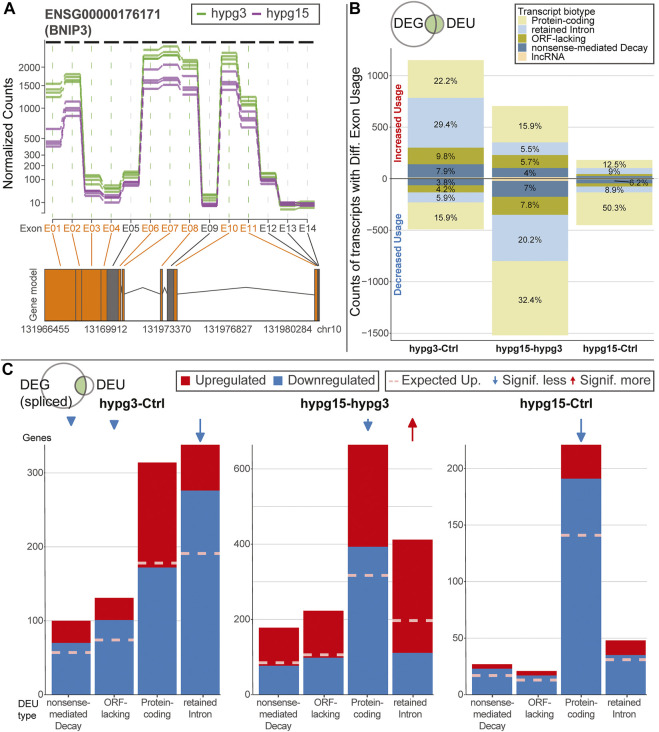
FIGURE 5.
Characterization of effects of alternative splicing. (A) Example of differential exon usage for the gene BCL2 interacting protein 3 (BNIP3) that carries the exon (E01) with the strongest differential effect for the contrast hypg15-hypg3, annotated in Figure 4A. Normalized counts of all exons are displayed over the entire gene. Exons that were flagged as significantly differentially used are highlighted in orange on the axis label and in the schematic gene model (exons as boxes, introns as triangles). (B) Distribution of transcript biotypes for all differentially used exons for all three temporal comparisons. Alterations in protein-coding exons still lead to translatable transcripts; transcripts with exons flagged as retained introns, processed transcripts and nonsense-mediated decay lead to transcripts that are not translated into proteins or show decreased translation rates and are likely prone to early degradation. The overall diminishing effect strength after 15 min of hypergravity can be observed, additionally the fraction of DEU transcripts that are not protein-coding is prominent after 3 min and decreased after 15 min. (C) Plotting of alternatively spliced transcripts from genes that, in addition to differential exon usage (DEU), are differentially expressed genes (DEGs). For each transcript, up- (red) or downregulation (blue) of the host gene is shown. This is based on the spliced pool since per definition the unspliced pool should not be informative about alternative splicing (compare Supplementary Figure S10 for unspliced data). Data is split by transcript biotype on the x axis. lncRNA has been excluded due to the small number. The expected fraction of upregulated genes is indicated by a dashed line, based on the fraction of upregulated versus downregulated genes for all genes multiplied with the number of DEG-DEU overlaps for the specified exon biotype. Protein-coding transcripts constitute the dominant fraction after 15 min but not after 3 min. After 3 min, DEUs with retained introns are the dominant group and are additionally much more downregulated than expected, as opposed to protein-coding DEUs after 3 min.