Figure 1. Perphenazine, DT‐061 and iHAP1 have no direct effect on PP2A holoenzymes.
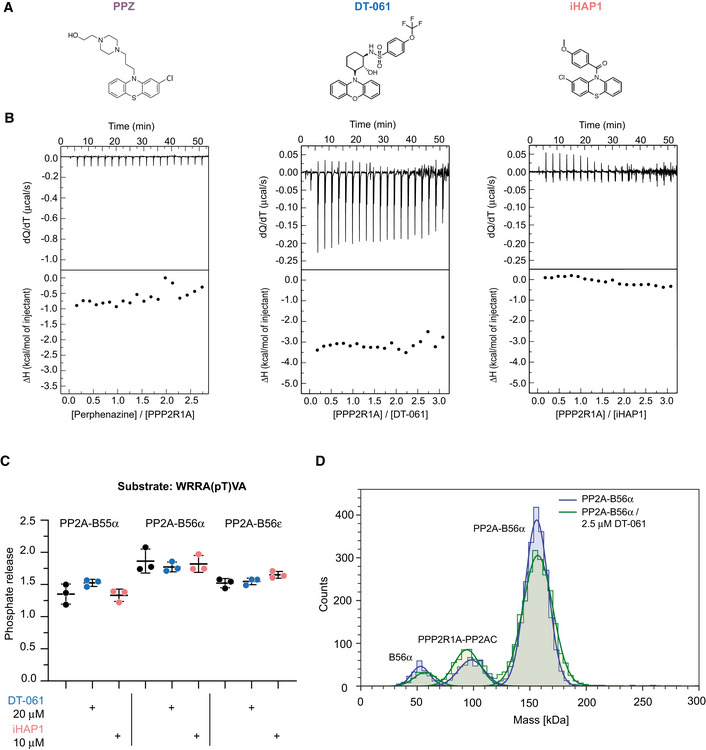
- Chemical structure of perphenazine, DT‐061 and iHAP1.
- Thermogram (top panel) for the calorimetric titration of perphenazine (400 μM, in syringe) in PPP2R1A (30 μM, in calorimetric cell) or PPP2R1A (300 μM, in syringe) in DT‐061 (20 μM, in calorimetric cell) or iHAP1 (20 μM, in calorimetric cell) at 25°C and corresponding ligand‐normalized integrated heats (bottom panel). Experiments were performed in 5% DMSO. At least two independent experiments were performed. Control injection of PPP2R1A shown in Fig EV1F.
- In vitro dephosphorylation assay using a basofilic phosphopeptide and purified PP2A holoenzymes. The peptide was incubated with specific PP2A holoenzymes together with iHAP1 or DT‐061 as indicated. The reaction was stopped after 15 min, and the amount of phosphate released directly measured. Mean and SD from three technical replicates of one out of three independent experiments are shown.
- MP mass distribution of the PP2A‐B56α holoenzyme at a final concentration of 50 nM in absence (blue) and in presence (green) of 2.5 µM DT‐061 in PBS. The mass photometry measurement of the holoenzyme shows a similar distribution of species in presence or absence of DT‐061. A representative experiment of two independent experiments is shown.
