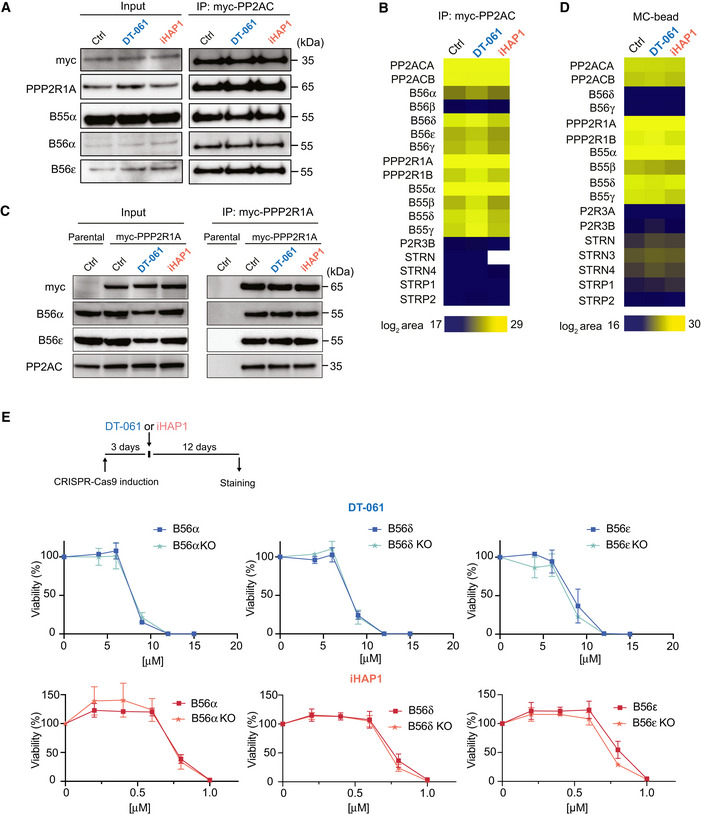
Figure 2. DT‐061 and iHAP1 toxicity is not affected by knockdown of specific B56 subunits.
-
A–CA stable inducible HEK‐293T cell line expressing myc‐PP2AC (panel A and B) and a stable inducible HeLa cell line expressing myc‐PP2R1A (C) were treated with DMSO, 20 μM DT‐061 or 2 μM iHAP1 for 30 min or 2 h respectively and myc‐PP2AC and myc‐PP2R1A affinity purified, respectively. The binding of the indicated proteins was analyzed by Western blotting (A and C) and myc‐PP2AC by quantitative mass spectrometry (B). (A) Representative of three independent experiments and (C) representative of two technical repeats and (B) analysis of a biological triplicate.
-
DHEK‐293T cells were treated with DMSO, 20 μM DT‐061 or 2 μM iHAP1 for 2 h, and protein lysates were incubated with a microcystin affinity column to capture PPP complexes. Bound complexes were analyzed by mass spectrometry to identify PP2A components. Analysis conducted on a biological triplicate.
-
EDoxycyclin‐inducible CRISPR‐Cas9 HeLa cell lines allow for depletion of specific B56 subunits. Growth assays in the presence of the indicated concentrations of DT‐061 or iHAP1 measured after 12 days of treatment. Mean and SD of three independent experiments are shown.
Source data are available online for this figure.
