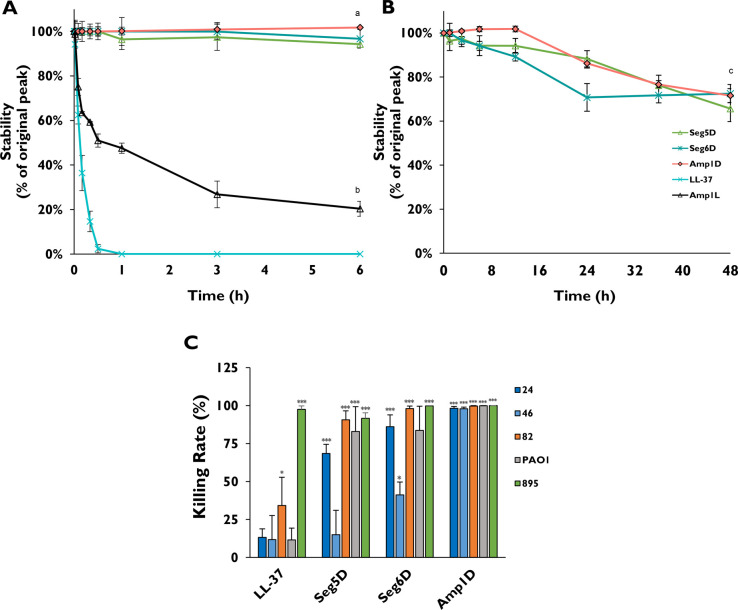
Figure 4.
AMPs stability and activity on P. aeruginosa CF isolates and PAO1 in the presence of CF sputum. Sputum samples from CF patients were pooled and diluted in a 1:10 ratio with PBS (for stability and killing assay). K6L9 peptides and LL-37 were added to the supernatant to a final concentration of 100 μM, and the mixture was incubated at 37 °C for various time intervals. Residual peptide concentrations were determined by RP-HPLC as described in the Experimental Section. (A) d,l-K6L9 peptides, Amp1L, and LL-37 for 6 h. (B) d,l-K6L9 for 48 h. (C) Killing rate assays were performed on P. aeruginosa CF isolates and PAO1. Bactria were cultured in 10% CF sputum, exposed for 1 h to 10 μM AMPs, and plated on LB agar plates. The significant difference in the peptide stability assay was determined by a linear mixed model fit by REML, and t tests use Satterthwaite’s method. (a) Significant difference between the l-amino peptides and the d,l-K6L9 peptides (p ≤ 0.001). (b) Significant difference between Amp1L and the d,l-K6L9 and LL-37 peptides (p ≤ 0.001). (c) Significant difference between the d,l-K6L9 peptides (p ≤ 0.05). The killing rate statistical significance from the untreated biofilm was determined by ANOVA.