FIGURE 1.
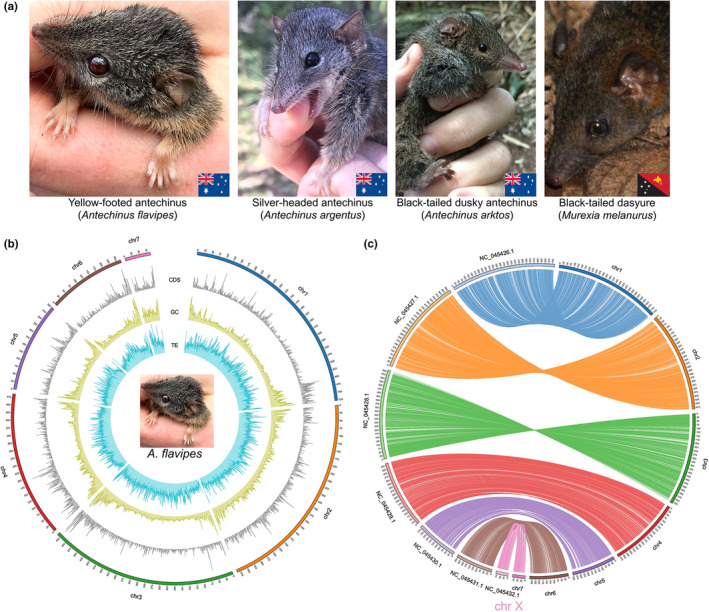
Overview of sequenced species and reference genome assemblies generated in this study. (a) Photographs of the five marsupial species sequenced. A yellow‐footed antechinus (Antechinus flavipes), silver‐headed antechinus (Antechinus argentus), and black‐tailed dusky antechinus (Antechinus arktos) from Australia; and a black‐tailed dasyure (Murexia melanurus) from Papua New Guinea. Antechinus spp. and M. melanurus photographs are courtesy of A.M.B. and John Hornbuckle, respectively. (b) Circos plot of the reference genome assembly of A. flavipes. The outermost segment represents chromosome sequences, with the numbers on the external surface indicating genome size in Mb. The line plots, from outside to inside, represent the distribution of CDS density (from 0 to 0.15), GC content (from 0.30 to 0.65) and TE ratio (from 0.2 to 1.0). Frequencies were calculated in 500‐kb sliding windows. (c) Circos plot showing shared synteny of A. flavipes (chr1‐chr7) and Sarcophilus harrisii (NC_045426.1‐NC_045432.1). Aligned using lastz. The synteny blocks are linked using lines coloured in accordance with the A. flavipes chromosomes. Aligned blocks with length shorter than 20 kb are not shown. Chr7 in A. flavipes corresponds to the X chromosome of Sarcophilus harrisii
