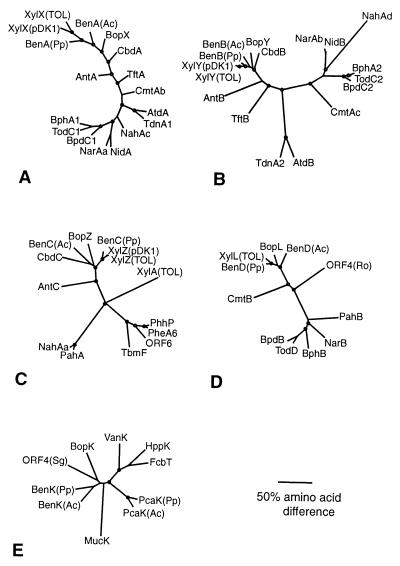
FIG. 6.
Phylogenetic trees based on comparisons with homologs of the Rhodococcus sp. strain 19070 Bop proteins. (A) BopX was aligned with alpha components of oxygenase subunits. (B) BopY was aligned with the corresponding beta components of oxygenases from Panel A (C) BopZ was aligned with available reductase components associated with oxygenases from panel A and other reductases or putative reductases. (D) The putative BopL dehydrogenase was aligned with dehydrogenases and putative dehydrogenases associated with the proteins displayed in trees A to C, as well as ORF4 (Ro). (E) BopK, a putative transport protein, was aligned with proteins that may be involved in transporting organic compounds. Gene clusters are associated with metabolism and/or transport of the indicated compounds: BopXYZLK, Rhodococcus sp. ATCC 19070, benzoate-toluate (AF279141), BenABCDK(Pp), P. putida strain PRS200, benzoate (AF218267), BenABCDK(Ac), Acinetobacter sp. strain ADP1, benzoate (AF009224), XylXYZ(pDK1), P. putida sp. plasmid pDK1, toluate (AF134348), XylXYZL(TOL), P. putida sp. TOL plasmid, benzoate (M64747), CbdABC, Burkholderia cepacia, halobenzoate (X79076), AntABC, Acinetobacter sp. strain ADP1, anthranilate (AF071556), TftAB, B. cepacia, 2,4,5-trichlorophenoxyacetic acid (U11420), AtdAB, Acinetobacter sp. plasmid pYA1, aniline (D86080), TdnA1B1, P. putida strain UCC22 (pTDN1) F1, aniline (D85415), CmtAbAcB, P. putida, p-cymene (U24215), NidAB, Rhodococcus sp. strain I24, indene (AF121905), NarAaAbB, Rhodococcus sp. strain NCIMB12038, naphthalene (AF082663), BphA1A2B, Rhodococcus sp. strain RHA1, biphenyl (D32142), NahAcAdAa, P. putida strain G7, napthalene (M83949), BpdC1C2B, Rhodococcus sp. strain M5, biphenyl-chlorobiphenyl (U27591), TodC1C2D, P. putida sp. strain F1, toluene (J04996), ORF6, A. calcoaceticus strain NCIB8250, phenol (Z36909), XylA, P. putida sp. TOL plasmid, xylene (M37480), PheA6, P. putida sp. strain BH, phenol (D28864), PhhP, P. putida sp. strain P35X (NCIB9869), phenol (X79063), TbmF, Pseudomonas sp. strain JS150, toluene-benzene (L40033), PahAB, P. aeruginosa strain PaK1, naphthalene (D84146), ORF4(Ro), Rhodococcus opacus sp. strain 1CP putative short-chain dehydrogenase (AF030176), PcaK(Ac), Acinetobacter sp. strain ADP1, protocatechuate transporter (L05770), ORF4(Sg), Streptomyces griseus, putative tyrosine transporter (AB022095), PcaK(Pp), P. putida sp. strain PRS2000, protocatechuate transporter (U10895), HppK, Rhodococcus globerulus sp. strain PWD1, putative 3-hydrox-yphenyl propionate transporter (U89712), FcbT, Arthrobacter sp. strain TM1, 4-chlorobenzoate transporter (AF042490), MucK, Acinetobacter sp. strain ADP1, cis,cis-muconate transporter (U87258), VanK, Acinetobacter sp. strain ADP1, vanillate transporter (AF009672). Accession numbers are indicated parenthetically. Circles represent branch points that occur with a frequency of 85 to 100%, respectively, as calculated by bootstrap analysis using 100 replicates.