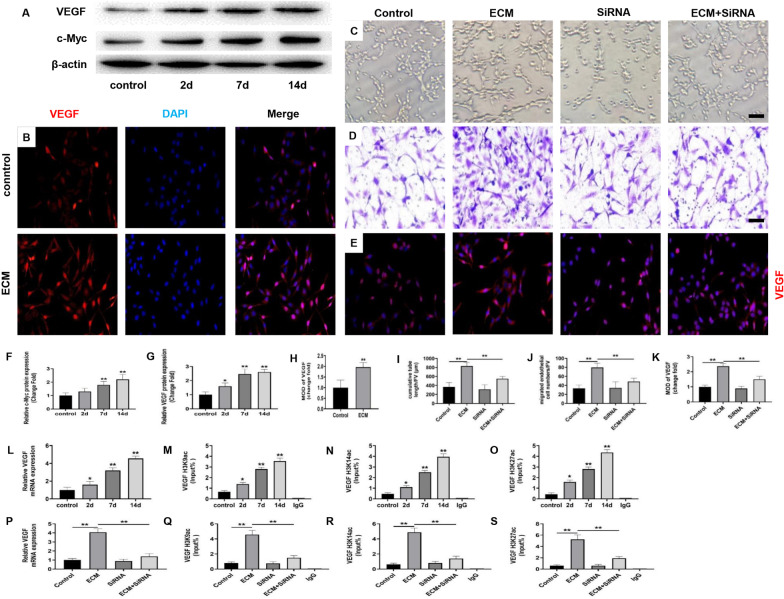
Fig. 2.
Cellular (c)-Myc mediated the increased expression of VEGF via histone acetylation modification in HUVECs induced by WJ-MSCs ECM. a, f, g Protein expression of VEGF and c-Myc in HUVECs was determined by western blotting. Mean ± S.E.M. n = 3. b Immunofluorescently stained for vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) of HUVECs (magnification: × 200). h The mean optical density (MOD) of VEGF expression was analyzed. Mean ± S.E.M. n = 3. c, i Matrigel tube formation assay images of cumulative tube length. Bar = 50 μm. Mean ± S.E.M., n = 3. d, j Transwell for HUVECs migration assay and quantitative analysis of migrated HUVEC numbers. Bar = 50 μm. Mean ± S.E.M., n = 3. e, k Immunofluorescently stained for VEGF of HUVECs (magnification: × 200). Bar = 50 μm. Mean ± S.E.M., n = 3. l, p mRNA expression of VEGF was determined by RT-qPCR. Mean ± S.E.M., n = 5. m–o, q–s The H3K9ac, H3K14ac and H3K27ac levels in the VEGF promoter region were determined by RT-qPCR. Mean ± S.E.M., n = 5. SiRNA: c-Myc SiRNA. The P value was calculated using one-way ANOVA and independent samples t-test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 versus control