FIGURE 1.
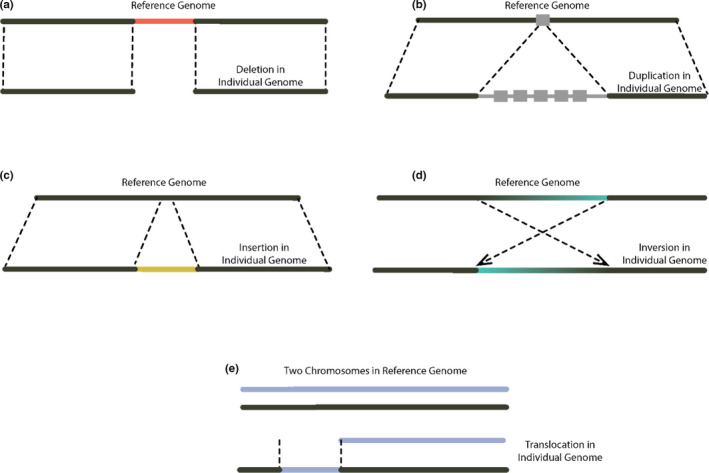
Structural variant (SV) types and how they differ from a reference genome: (a) deletion, where a segment of DNA is not present in an individual, but present in the reference; (b) duplication, a rearrangement where there is more than one copy of a particular region of the genome, often in tandem. These can be either intrachromosomal, as shown here, or interchromosomal; (c) insertion, a DNA sequence present in an individual sample, but not present in the reference; (d) inversion, a segment of the chromosome that has had a double‐stranded break at an upstream and downstream location and become reversed in order; (e) translocation, a rearrangement where a portion of one chromosome has been transposed onto another
