FIGURE 1.
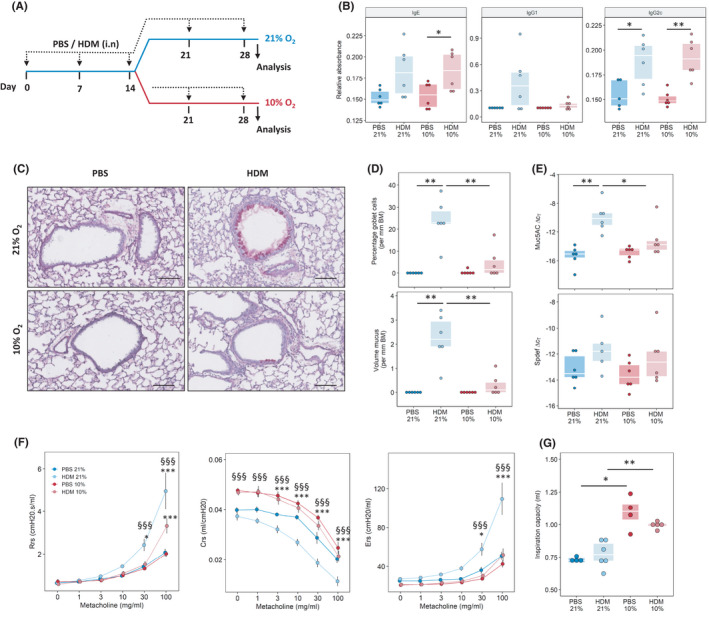
Reduced oxygen concentrations decrease house dust mite (HDM) induced goblet cell hyperplasia and airway hyper‐reactivity. (A) Experimental outline. Mice were sensitized and challenged with a crude extract of HDM or PBS once a week over 4 weeks; after 2 weeks, mice kept under room air (21% oxygen) or reduced oxygen conditions (10% oxygen) for an additional 2 weeks. Analysis was performed 72 h after the last challenge. (B) Serum levels of HDM‐specific antibodies. (C) Periodic acid‐Schiff (PAS) staining of mouse lung tissue isolated from mice exposed to HDM or PBS for 4 weeks with or without the additional exposure to 10% O2, scale bar indicates 100 µm. (D) Quantification of goblet cell hyperplasia and mucus levels, basement membrane (BM). (E) Quantitative PCR analysis of Muc5AC and Spdef expression in lung tissue. (F) Assessment of airway hyper‐responsiveness and induced by exposure to increasing methacholine (MCh) concentrations; airway resistance (Rrs), compliance (Crs) and elastance (Ers). (G) Inspired capacity (IC) *p < .05, ***p < .001 vs. respective PBS, §§§p < .001 vs. HDM (10% O2)
