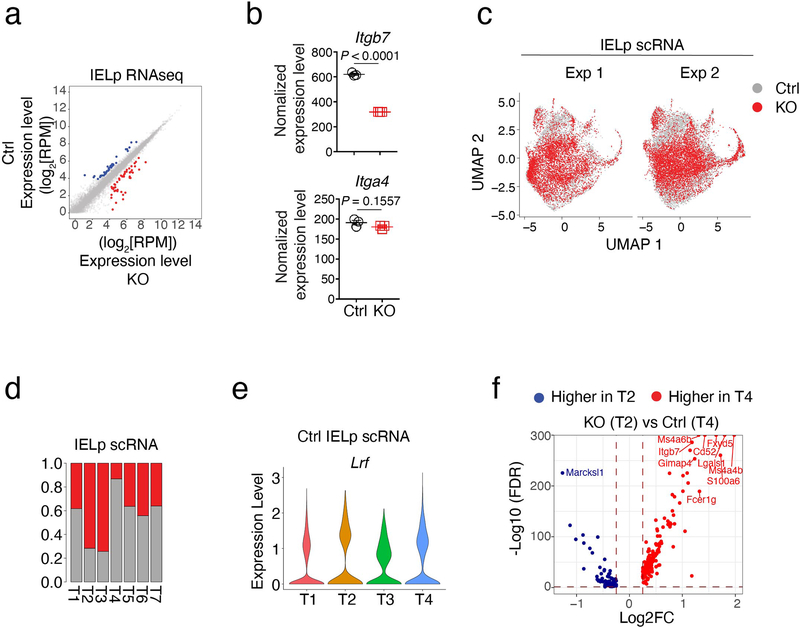
Extended Data Fig. 5. Control of IELp gene expression by LRF.
(a-b) Population RNAseq of thymic IELp.
(a) Scatter plots compare gene expression (Log2 values, full gene set) in Ctrl vs. KO IELp. Genes with two-fold or greater differential expression between genotypes (and FDR<0.01) are shown in blue or red.
(b) RNAseq expression levels (counts per million) of Itgb7 and Itga4 genes in IELp from Ctrl and KO mice. Error bars indicate SEM. P values are from two-tailed unpaired t-test.
(c-f) ScRNAseq of thymic IELp from Ctrl and KO mice.
(c) UMAP analysis of IELp, performed as in Fig. 5a, displayed separately for each experiment and color-coded by genotype.
(d) Bar plots indicate the Ctrl (gray) vs. LRF KO (red) genotype distribution of IELp clusters referred to in Fig. 5a,b.
(e) Violin plot shows the expression of Lrf in indicated clusters from Ctrl IELp.
(f) Volcano plot showing differentially expressed genes (FDR<0.05, |Log2FC| >0.25) between Ctrl T4 (mature) and LRF KO T2 (intermediate) IELp clusters. Blue and red symbols indicate genes preferentially expressed in KO and Ctrl IELp, respectively.