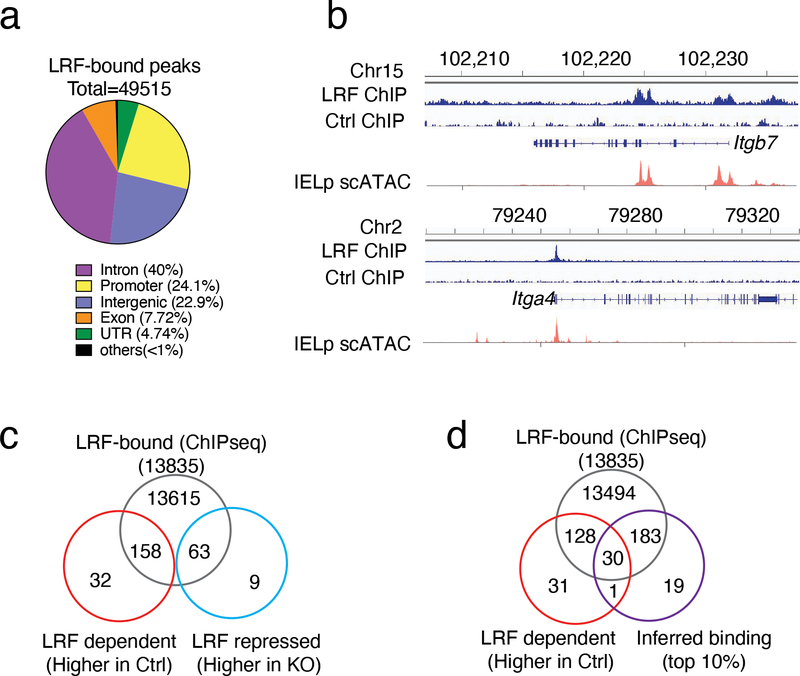
Figure 6. LRF binds the Itgb7 locus.
(a, b) LRF ChIP-seq in activated CD4+ T cells from Rosa26BirA+ mice transduced with LrfBio retrovirus (LRF ChIP) or empty retrovirus (Thy1.1 expressing, Ctrl ChIP).
(a) Pie chart shows the genome-wide distribution of LRF ChIPseq binding sites in activated T cells.
(b) Peaks show LRF binding sites in Itgb7 and Itga4 genes. For each gene, bottom tracks (scATAC) show chromatin accessibility in IELp.
(c) Venn diagrams show overlap between the sets of LRF-binding genes (ChIPseq, top), and genes preferentially expressed in Ctrl (LRF-dependent, bottom left) or LRF KO (LRF-repressed genes, bottom right) IELp, as defined in Extended Data Fig. 5f.
(d) Venn diagrams show intersection between the sets of LRF-binding genes (ChIPseq), scRNAseq-defined LRF-dependent genes (defined in Extended Data Fig. 5f) and the top 10% genes inferred as LRF targets by CellOracle.